Management of chronic liver disease pdf
Relationships Between Nutrition, Alcohol Use, and Liver Disease Charles S. Lieber, M.D., M.A.C.P. Many alcoholics are malnourished, either because they ingest too
Chronic liver disease is increasingly prevalent and, as the population ages, geriatricians will see an increasing burden. We present an overview of the investigation and management of older adults with chronic parenchymal liver disease and highlight the potential roles of transjugular intrahepatic portosytemic shunts and orthotopic liver transplantation.
these guidelines to help with the management of nutritional problems in patients with liver cirrhosis. For clarity, the terms and definitions used in the present CPGs are summarised (Box 1). Screening and assessment for malnutrition and obesity in liver cirrhosis: Who, when and how Given the worse prognosis associated with malnutrition, all patients with advanced chronic liver disease, and in
Chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C represent about 8% of all cases of chronic liver disease in Australia. The rising prevalence of chronic liver disease contributes to increasing rates of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
DIET AND NUTRITION FOR LIVER DISEASE AND HEPATITIS By Dr . Hassan El Shennawy Prof. of medicine National Liver Institute Menoufya Universty. Contents : Introduction DIET IN ACUTE LIVER DISEASE DIET IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE DIET AS A CAUSE OF LIVER DISEASE DRUG NUTRIENT INTERACTION. Questions frequently asked by liver diseased patient concerning diet …
End Stage Liver Failure Aetiology of Chronic Liver Disease – Neonatal liver disease – Chronic hepatitis – Metabolic – Fibropolycystic liver disease
Management of End-Stage Liver Disease in Chronic Hepatitis B Hui-Hui Tan, MBBS, MRCPa,*, Paul Martin, MD, FRCP, FRCPIb Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the most common cause of chronic …
Efficacy of a Chronic Disease Management Model for Patients With Chronic Liver Failure ALAN J. WIGG,* ROSEMARY MCCORMICK,* RACHEL WUNDKE,* and RICHARD J. WOODMAN‡
Chronic Disease Management Schedule Checklist – a reminder summary of when to claim and schedule in best care for your chronic disease clients Putting the Patient in the Picture resource – general practice clinics including systems and data management, setting up and implementing the clinic, and self-management and prevention.
Download file Free Book PDF Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart at Complete PDF Library. This Book have some digital formats such us : paperbook, ebook, kindle, epub, and another formats. Here is The Complete PDF Book Library. It’s free to register here to get Book file PDF Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart. Decompensated alcohol related liver disease …
The management of children with chronic liver disease (CLD) mandates a multidisciplinary approach. CLDs can be classified into ‘potentially’ curable, treatable non-curable, and end-stage diseases.
Diamond T, Stiel D, Mason R, Lissner D, Bikle D, Wilson S, Posen S. Serum vitamin D metabolites are not responsible for low turnover osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Dec; 69 (6):1234–1239.
Plasma immunoreactive beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in chronic liver disease and fulminant hepatic failure. J Invest Dermatol 1978 ; 70 : 326 – 327 . Barton JC , McDonnell SM , Adams PC , et al. Management of hemochromatosis.
Chronic Liver Disease Life in the Fast Lane Medical Blog
https://youtube.com/watch?v=f-Fxlsb2dtQ

Nutrition management in chronic liver disease SpringerLink
Malnutrition in chronic liver disease is better defined as protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) because kwashiorkor- like malnutrition and marasmus frequently coexist (3, 4).
Renal function is often impaired in chronic liver disease and may be an important factor to consider in drug management. The management strategy of any liver disease is a combination of treating the symptoms and complications that arise, as well as drug therapies relevant to …
The main complications of the patient with liver disease are risk of contagion (for healthcare personnel and other patients), the risk of bleeding and the risk of toxicity due …
Chronic cholestasis is a well-accepted risk factor for osteopenia [53 x [53] Collier, J.D., Ninkovic, M., and Compston, J.E. Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated with chronic liver disease.
associated with liver failure, (3) interpretation of biochemical test of liver disease and failure, (4) ancillary tests used in evaluation and management of equine liver failure, and (5) treatment and prognosis of liver failure.
Chronic Disease Management (CDM) is a patient-centered approach to healthcare delivery that emphasizes proactive, longitudinal care between visits. Most healthcare systems are still based on acute illness disease models established at the beginning of the 20th century. In contrast, chronic illnesses now account for more than 75% of total healthcare expenditures.
REVIEW ARTICLE Management of Thrombocytopenia in Chronic Liver Disease: Focus on Pharmacotherapeutic Strategies Raoel Maan1 • Robert J. de Knegt1 • Bart J. Veldt1
Liver has a central role in nutritional homeostasis and any liver disease leads to abnormalities in nutrient metabolism and subsequent malnutrition. All children with chronic liver disease (CLD) must undergo a periodic nutritional assessment — medical history, anthropometry esp. skinfold thickness
the disease status, indication for therapy, therapeutic options, advantage, possible risk, and problems of the therapies is crucial for good compliance with therapy and
Value ofLiver Biopsy in the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Liver Disease in Renal Transplant Recipients K. VENKATESWARARAo, M.D., W. ROBERT ANDERSON, M.D
Improved medical management and the changing disease demographic mean that the majority of patients with chronic liver disease are living with the disease rather than dying from it.
with unexplained acute and chronic liver injury, as well as when prescribing certain gastrointestinal medications (e.g., azathio- prine, anti-tumor necrosis factor agents, sulfonamides) ( 7,8 ).
of liver transplants, the clinical features of liver disease, and the medical and dental management of children before and after liver transplantation.(Pediatr Dent 21:273-281, 1999)

to download a pdf or request a hard copy. th 2 Forewor d This third edition of Chronic Kidney This third edition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice is the synthesis of the evolving evidence that the management of kidney disease matters. The Kidney Check Australia Task Force (KCAT) -now in its 13 year- has produced this book in the hope that practitioners will
therapies for patients with liver disease, liver biopsy and histological assessment of the liver has now taken on an important role in clinical management. Therefore, as of 2009, liver biopsy currently has three major roles: (1) for diagnosis, (2) for assessment of prognosis (disease stag-ing), and/or (3) to assist in making therapeutic manage-ment decisions. Diagnosis. For many diseases
7/8/2016 1 Ryan M. Ford, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Transplant Hepatology Director of Viral Hepatitis Emory Transplant Center 7. Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)
care management and the use of emergency liver transplantation.5 In this review, with chronic liver disease and often result from idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury or are indeterminate
Liver Disease Management and Care of Patients 6KNIN337
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases. Edited by Anne M. Larson. Volume 98, Issue 1, Pages 1-180 (January 2014) Previous vol/issue. Next vol/issue. Select all documents. Download PDFs. Export. Show all article previews Show all article previews. select article CME Accreditation Page and Author Disclosures. Examination Full text access CME Accreditation Page and Author …
Module aim This module will enable practitioners to develop their knowledge base in caring for patients with liver disease. The focus will predominately be on chronic liver disease, although the course will
Chronic liver disease is a widespread pathology characterized by a progression from steatosis to chronic hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Recent epidemiological and experimental researches indicate that oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of liver disorders. Carotenoids exist in abundance in fruit and vegetables and have been known to
liver disease, a joint single topic conference was recently sponsored by the Brazilian Society of Hepatology in cooperation with the Brazilian Society of Intensive Care Medicine and the Brazilian Association for Organ Transplantation.
Cirrhosis is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally. Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The damage to your liver builds up over time. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. It lies up under your ribs on the right side of
The Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD)—and PELD, the pediatric model—use bilirubin, creatinine, and international normalized ratio values to classify disease severity. MELD and PELD scores are considered more accurate than the Child-Pugh score in determining short-term mortality, 16 and are used by the United Network of Organ Sharing (UNOS) for liver allocation.
SUPPLEMENT Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated with chronic liver disease J D Collier, M Ninkovic, J E Compston….. Gut2002;50(Suppl I):i1–i9
chronic liver disease and hepatic and extrahepatic organ failures, and is associated with substantial short-term mortality. Common precipitants include bacterial and viral infections, alcoholic hepatitis, and surgery, but in more
Conventional wisdom is that chronic liver disease is an acquired bleeding disorder. However, the imbalance between procoagulant and anticoagulant activities can also lead to thrombosis. Studies
Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Management of End-Stage Liver Disease in Chronic Hepatitis B
Liver failure or hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic. [1]
tions caused by chronic liver disease. Introduction Cirrhosis results in around 29,000 deaths annually in the United States. Patients with cirrhosis who do not receive a liver transplant have a 5-year mortality rate of up to 85%. Cirrhosis is the result of chronic inflamma-tion and development of fibrosis that leads to various complications of chronic liver disease. These complica-tions are
The effect that chronic liver disease has on a child’s nutritional status and health is determined by the cause and severity of the liver disease and the age of onset.
Fluid and Electrolyte Management in Chronic Liver Disease Most patients with ascites caused by cirrhosis have an impaired renal handling of water that results in dilutional hyponatremia, the severity of which correlates directly with the severity of liver disease.
While chronic kidney disease (CKD), low albumin, and high Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)-Na score were found to be statistically significant predictors of morbidity. Addition of sepsis in conventional MELD score predicted mortality even better than MELD-Na (area under receiver operating characteristic: 0.735 vs 0.686; P < 0.001).
(PDF) Medical Management of Chronic Liver Diseases in
SUPPLEMENT Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis
10/03/2015 · Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Childhood liver disorders have, in general, mode of presentations which are distinct from that in adult population. It is due to varying etiology and natural history of the liver diseases in
Diagnosis and management of bone disease in patients with chronic liver disease. *Calcium (1,000–1,500 mg/d) and 25(OH)D (400–800 IU/d or 260 µg every two weeks) to preserve normal levels. **According to the severity of liver disease and cholestasis, and in patients taking corticosteroids.
Absence of chronic liver disease b. Acute transaminitis (ALT/AST) c. Coagulopathy with INR > 1.3 d. Evidence of encephalopathy e. Illness duration < 28 days d. Concerning the management of neurological complications in ALF: a. Target PaCO 2 is that of low-normal range b. Hypertonic saline is a recognised treatment for cerebral oedema c. All patients should have invasive intra-cranial pressure
Management of chronic liver disease Request PDF

A chronic disease management model for chronic liver
Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated


Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Children
Management of Pruritus in Chronic Liver Disease Europe
Recognizing and treating cutaneous signs of liver disease

INTENSIVE CARE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH LIVER DISEASE
Value ofLiver Biopsy in the Evaluation and Management of
Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart
(PDF) Medical Management of Chronic Liver Diseases in
of liver transplants, the clinical features of liver disease, and the medical and dental management of children before and after liver transplantation.(Pediatr Dent 21:273-281, 1999)
The effect that chronic liver disease has on a child’s nutritional status and health is determined by the cause and severity of the liver disease and the age of onset.
Value ofLiver Biopsy in the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Liver Disease in Renal Transplant Recipients K. VENKATESWARARAo, M.D., W. ROBERT ANDERSON, M.D
Chronic liver disease is a widespread pathology characterized by a progression from steatosis to chronic hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Recent epidemiological and experimental researches indicate that oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of liver disorders. Carotenoids exist in abundance in fruit and vegetables and have been known to
Childhood liver disorders have, in general, mode of presentations which are distinct from that in adult population. It is due to varying etiology and natural history of the liver diseases in
While chronic kidney disease (CKD), low albumin, and high Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)-Na score were found to be statistically significant predictors of morbidity. Addition of sepsis in conventional MELD score predicted mortality even better than MELD-Na (area under receiver operating characteristic: 0.735 vs 0.686; P < 0.001).
Chronic liver disease is increasingly prevalent and, as the population ages, geriatricians will see an increasing burden. We present an overview of the investigation and management of older adults with chronic parenchymal liver disease and highlight the potential roles of transjugular intrahepatic portosytemic shunts and orthotopic liver transplantation.
Recognizing and treating cutaneous signs of liver disease
SUPPLEMENT Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis
therapies for patients with liver disease, liver biopsy and histological assessment of the liver has now taken on an important role in clinical management. Therefore, as of 2009, liver biopsy currently has three major roles: (1) for diagnosis, (2) for assessment of prognosis (disease stag-ing), and/or (3) to assist in making therapeutic manage-ment decisions. Diagnosis. For many diseases
The effect that chronic liver disease has on a child’s nutritional status and health is determined by the cause and severity of the liver disease and the age of onset.
The Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD)—and PELD, the pediatric model—use bilirubin, creatinine, and international normalized ratio values to classify disease severity. MELD and PELD scores are considered more accurate than the Child-Pugh score in determining short-term mortality, 16 and are used by the United Network of Organ Sharing (UNOS) for liver allocation.
Chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C represent about 8% of all cases of chronic liver disease in Australia. The rising prevalence of chronic liver disease contributes to increasing rates of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
chronic liver disease and hepatic and extrahepatic organ failures, and is associated with substantial short-term mortality. Common precipitants include bacterial and viral infections, alcoholic hepatitis, and surgery, but in more
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases
Nutrition fluid and electrolytes in chronic liver disease
Liver failure or hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic. [1]
liver disease, a joint single topic conference was recently sponsored by the Brazilian Society of Hepatology in cooperation with the Brazilian Society of Intensive Care Medicine and the Brazilian Association for Organ Transplantation.
Childhood liver disorders have, in general, mode of presentations which are distinct from that in adult population. It is due to varying etiology and natural history of the liver diseases in
the disease status, indication for therapy, therapeutic options, advantage, possible risk, and problems of the therapies is crucial for good compliance with therapy and
therapies for patients with liver disease, liver biopsy and histological assessment of the liver has now taken on an important role in clinical management. Therefore, as of 2009, liver biopsy currently has three major roles: (1) for diagnosis, (2) for assessment of prognosis (disease stag-ing), and/or (3) to assist in making therapeutic manage-ment decisions. Diagnosis. For many diseases
Fluid and Electrolyte Management in Chronic Liver Disease Most patients with ascites caused by cirrhosis have an impaired renal handling of water that results in dilutional hyponatremia, the severity of which correlates directly with the severity of liver disease.
Management of End-Stage Liver Disease in Chronic Hepatitis B Hui-Hui Tan, MBBS, MRCPa,*, Paul Martin, MD, FRCP, FRCPIb Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the most common cause of chronic …
The main complications of the patient with liver disease are risk of contagion (for healthcare personnel and other patients), the risk of bleeding and the risk of toxicity due …
The management of children with chronic liver disease (CLD) mandates a multidisciplinary approach. CLDs can be classified into ‘potentially’ curable, treatable non-curable, and end-stage diseases.
Diagnosis and management of bone disease in patients with chronic liver disease. *Calcium (1,000–1,500 mg/d) and 25(OH)D (400–800 IU/d or 260 µg every two weeks) to preserve normal levels. **According to the severity of liver disease and cholestasis, and in patients taking corticosteroids.
Chronic liver disease is a widespread pathology characterized by a progression from steatosis to chronic hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Recent epidemiological and experimental researches indicate that oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of liver disorders. Carotenoids exist in abundance in fruit and vegetables and have been known to
associated with liver failure, (3) interpretation of biochemical test of liver disease and failure, (4) ancillary tests used in evaluation and management of equine liver failure, and (5) treatment and prognosis of liver failure.
Malnutrition in chronic liver disease is better defined as protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) because kwashiorkor- like malnutrition and marasmus frequently coexist (3, 4).
The effect that chronic liver disease has on a child’s nutritional status and health is determined by the cause and severity of the liver disease and the age of onset.
Recognizing and treating cutaneous signs of liver disease
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases
Chronic cholestasis is a well-accepted risk factor for osteopenia [53 x [53] Collier, J.D., Ninkovic, M., and Compston, J.E. Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated with chronic liver disease.
10/03/2015 · Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
While chronic kidney disease (CKD), low albumin, and high Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)-Na score were found to be statistically significant predictors of morbidity. Addition of sepsis in conventional MELD score predicted mortality even better than MELD-Na (area under receiver operating characteristic: 0.735 vs 0.686; P < 0.001).
chronic liver disease and hepatic and extrahepatic organ failures, and is associated with substantial short-term mortality. Common precipitants include bacterial and viral infections, alcoholic hepatitis, and surgery, but in more
Cirrhosis is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally. Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The damage to your liver builds up over time. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. It lies up under your ribs on the right side of
Liver has a central role in nutritional homeostasis and any liver disease leads to abnormalities in nutrient metabolism and subsequent malnutrition. All children with chronic liver disease (CLD) must undergo a periodic nutritional assessment — medical history, anthropometry esp. skinfold thickness
Chronic liver disease is a widespread pathology characterized by a progression from steatosis to chronic hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Recent epidemiological and experimental researches indicate that oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of liver disorders. Carotenoids exist in abundance in fruit and vegetables and have been known to
care management and the use of emergency liver transplantation.5 In this review, with chronic liver disease and often result from idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury or are indeterminate
Management of Pruritus in Chronic Liver Disease Europe
Chronic Liver Disease Life in the Fast Lane Medical Blog
SUPPLEMENT Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated with chronic liver disease J D Collier, M Ninkovic, J E Compston….. Gut2002;50(Suppl I):i1–i9
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases. Edited by Anne M. Larson. Volume 98, Issue 1, Pages 1-180 (January 2014) Previous vol/issue. Next vol/issue. Select all documents. Download PDFs. Export. Show all article previews Show all article previews. select article CME Accreditation Page and Author Disclosures. Examination Full text access CME Accreditation Page and Author …
Efficacy of a Chronic Disease Management Model for Patients With Chronic Liver Failure ALAN J. WIGG,* ROSEMARY MCCORMICK,* RACHEL WUNDKE,* and RICHARD J. WOODMAN‡
the disease status, indication for therapy, therapeutic options, advantage, possible risk, and problems of the therapies is crucial for good compliance with therapy and
Management of End-Stage Liver Disease in Chronic Hepatitis B Hui-Hui Tan, MBBS, MRCPa,*, Paul Martin, MD, FRCP, FRCPIb Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the most common cause of chronic …
The effect that chronic liver disease has on a child’s nutritional status and health is determined by the cause and severity of the liver disease and the age of onset.
Chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C represent about 8% of all cases of chronic liver disease in Australia. The rising prevalence of chronic liver disease contributes to increasing rates of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
associated with liver failure, (3) interpretation of biochemical test of liver disease and failure, (4) ancillary tests used in evaluation and management of equine liver failure, and (5) treatment and prognosis of liver failure.
Relationships Between Nutrition, Alcohol Use, and Liver Disease Charles S. Lieber, M.D., M.A.C.P. Many alcoholics are malnourished, either because they ingest too
Chronic liver disease is a widespread pathology characterized by a progression from steatosis to chronic hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Recent epidemiological and experimental researches indicate that oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of liver disorders. Carotenoids exist in abundance in fruit and vegetables and have been known to
Diamond T, Stiel D, Mason R, Lissner D, Bikle D, Wilson S, Posen S. Serum vitamin D metabolites are not responsible for low turnover osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Dec; 69 (6):1234–1239.
Improved medical management and the changing disease demographic mean that the majority of patients with chronic liver disease are living with the disease rather than dying from it.
Diagnosis and management of chronic liver disease in older
A chronic disease management model for chronic liver
chronic liver disease and hepatic and extrahepatic organ failures, and is associated with substantial short-term mortality. Common precipitants include bacterial and viral infections, alcoholic hepatitis, and surgery, but in more
7/8/2016 1 Ryan M. Ford, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Transplant Hepatology Director of Viral Hepatitis Emory Transplant Center 7. Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)
Diagnosis and management of bone disease in patients with chronic liver disease. *Calcium (1,000–1,500 mg/d) and 25(OH)D (400–800 IU/d or 260 µg every two weeks) to preserve normal levels. **According to the severity of liver disease and cholestasis, and in patients taking corticosteroids.
Diamond T, Stiel D, Mason R, Lissner D, Bikle D, Wilson S, Posen S. Serum vitamin D metabolites are not responsible for low turnover osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Dec; 69 (6):1234–1239.
tions caused by chronic liver disease. Introduction Cirrhosis results in around 29,000 deaths annually in the United States. Patients with cirrhosis who do not receive a liver transplant have a 5-year mortality rate of up to 85%. Cirrhosis is the result of chronic inflamma-tion and development of fibrosis that leads to various complications of chronic liver disease. These complica-tions are
therapies for patients with liver disease, liver biopsy and histological assessment of the liver has now taken on an important role in clinical management. Therefore, as of 2009, liver biopsy currently has three major roles: (1) for diagnosis, (2) for assessment of prognosis (disease stag-ing), and/or (3) to assist in making therapeutic manage-ment decisions. Diagnosis. For many diseases
the disease status, indication for therapy, therapeutic options, advantage, possible risk, and problems of the therapies is crucial for good compliance with therapy and
these guidelines to help with the management of nutritional problems in patients with liver cirrhosis. For clarity, the terms and definitions used in the present CPGs are summarised (Box 1). Screening and assessment for malnutrition and obesity in liver cirrhosis: Who, when and how Given the worse prognosis associated with malnutrition, all patients with advanced chronic liver disease, and in
Chronic Disease Management (CDM) is a patient-centered approach to healthcare delivery that emphasizes proactive, longitudinal care between visits. Most healthcare systems are still based on acute illness disease models established at the beginning of the 20th century. In contrast, chronic illnesses now account for more than 75% of total healthcare expenditures.
Renal function is often impaired in chronic liver disease and may be an important factor to consider in drug management. The management strategy of any liver disease is a combination of treating the symptoms and complications that arise, as well as drug therapies relevant to …
While chronic kidney disease (CKD), low albumin, and high Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)-Na score were found to be statistically significant predictors of morbidity. Addition of sepsis in conventional MELD score predicted mortality even better than MELD-Na (area under receiver operating characteristic: 0.735 vs 0.686; P < 0.001).
Fluid and Electrolyte Management in Chronic Liver Disease Most patients with ascites caused by cirrhosis have an impaired renal handling of water that results in dilutional hyponatremia, the severity of which correlates directly with the severity of liver disease.
care management and the use of emergency liver transplantation.5 In this review, with chronic liver disease and often result from idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury or are indeterminate
251 Acute Liver Failure in Critical Care Anaesthesia UK
Chronic Liver Disease/Cirrhosis Johns Hopkins Medicine
10/03/2015 · Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Module aim This module will enable practitioners to develop their knowledge base in caring for patients with liver disease. The focus will predominately be on chronic liver disease, although the course will
Improved medical management and the changing disease demographic mean that the majority of patients with chronic liver disease are living with the disease rather than dying from it.
chronic liver disease and hepatic and extrahepatic organ failures, and is associated with substantial short-term mortality. Common precipitants include bacterial and viral infections, alcoholic hepatitis, and surgery, but in more
Chronic liver disease is a widespread pathology characterized by a progression from steatosis to chronic hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Recent epidemiological and experimental researches indicate that oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of liver disorders. Carotenoids exist in abundance in fruit and vegetables and have been known to
Value ofLiver Biopsy in the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Liver Disease in Renal Transplant Recipients K. VENKATESWARARAo, M.D., W. ROBERT ANDERSON, M.D
Relationships Between Nutrition, Alcohol Use, and Liver Disease Charles S. Lieber, M.D., M.A.C.P. Many alcoholics are malnourished, either because they ingest too
Malnutrition in chronic liver disease is better defined as protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) because kwashiorkor- like malnutrition and marasmus frequently coexist (3, 4).
these guidelines to help with the management of nutritional problems in patients with liver cirrhosis. For clarity, the terms and definitions used in the present CPGs are summarised (Box 1). Screening and assessment for malnutrition and obesity in liver cirrhosis: Who, when and how Given the worse prognosis associated with malnutrition, all patients with advanced chronic liver disease, and in
Chronic Disease Management Schedule Checklist – a reminder summary of when to claim and schedule in best care for your chronic disease clients Putting the Patient in the Picture resource – general practice clinics including systems and data management, setting up and implementing the clinic, and self-management and prevention.
Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
The Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD)—and PELD, the pediatric model—use bilirubin, creatinine, and international normalized ratio values to classify disease severity. MELD and PELD scores are considered more accurate than the Child-Pugh score in determining short-term mortality, 16 and are used by the United Network of Organ Sharing (UNOS) for liver allocation.
SUPPLEMENT Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated with chronic liver disease J D Collier, M Ninkovic, J E Compston….. Gut2002;50(Suppl I):i1–i9
Cirrhosis is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally. Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The damage to your liver builds up over time. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. It lies up under your ribs on the right side of
Chronic Disease Management (CDM) is a patient-centered approach to healthcare delivery that emphasizes proactive, longitudinal care between visits. Most healthcare systems are still based on acute illness disease models established at the beginning of the 20th century. In contrast, chronic illnesses now account for more than 75% of total healthcare expenditures.
Liver Disease Management and Care of Patients 6KNIN337
Nutrition management in chronic liver disease SpringerLink
Liver has a central role in nutritional homeostasis and any liver disease leads to abnormalities in nutrient metabolism and subsequent malnutrition. All children with chronic liver disease (CLD) must undergo a periodic nutritional assessment — medical history, anthropometry esp. skinfold thickness
Chronic Disease Management (CDM) is a patient-centered approach to healthcare delivery that emphasizes proactive, longitudinal care between visits. Most healthcare systems are still based on acute illness disease models established at the beginning of the 20th century. In contrast, chronic illnesses now account for more than 75% of total healthcare expenditures.
Liver failure or hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic. [1]
to download a pdf or request a hard copy. th 2 Forewor d This third edition of Chronic Kidney This third edition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice is the synthesis of the evolving evidence that the management of kidney disease matters. The Kidney Check Australia Task Force (KCAT) -now in its 13 year- has produced this book in the hope that practitioners will
therapies for patients with liver disease, liver biopsy and histological assessment of the liver has now taken on an important role in clinical management. Therefore, as of 2009, liver biopsy currently has three major roles: (1) for diagnosis, (2) for assessment of prognosis (disease stag-ing), and/or (3) to assist in making therapeutic manage-ment decisions. Diagnosis. For many diseases
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases. Edited by Anne M. Larson. Volume 98, Issue 1, Pages 1-180 (January 2014) Previous vol/issue. Next vol/issue. Select all documents. Download PDFs. Export. Show all article previews Show all article previews. select article CME Accreditation Page and Author Disclosures. Examination Full text access CME Accreditation Page and Author …
chronic liver disease and hepatic and extrahepatic organ failures, and is associated with substantial short-term mortality. Common precipitants include bacterial and viral infections, alcoholic hepatitis, and surgery, but in more
Malnutrition in chronic liver disease is better defined as protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) because kwashiorkor- like malnutrition and marasmus frequently coexist (3, 4).
Efficacy of a Chronic Disease Management Model for Patients With Chronic Liver Failure ALAN J. WIGG,* ROSEMARY MCCORMICK,* RACHEL WUNDKE,* and RICHARD J. WOODMAN‡
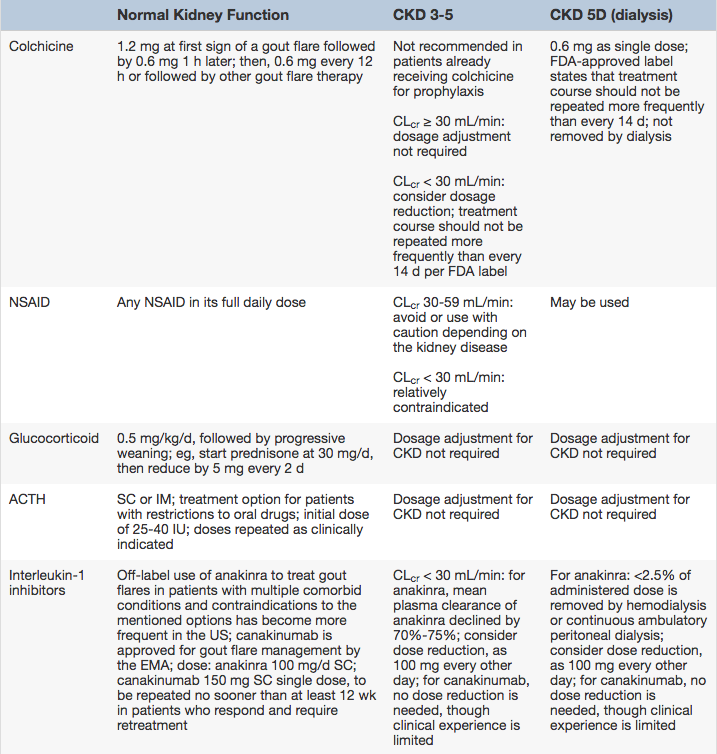
REVIEW ARTICLE Management of Thrombocytopenia in Chronic Liver Disease: Focus on Pharmacotherapeutic Strategies Raoel Maan1 • Robert J. de Knegt1 • Bart J. Veldt1
of liver transplants, the clinical features of liver disease, and the medical and dental management of children before and after liver transplantation.(Pediatr Dent 21:273-281, 1999)
Chronic liver disease is a widespread pathology characterized by a progression from steatosis to chronic hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Recent epidemiological and experimental researches indicate that oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of liver disorders. Carotenoids exist in abundance in fruit and vegetables and have been known to
care management and the use of emergency liver transplantation.5 In this review, with chronic liver disease and often result from idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury or are indeterminate
Cirrhosis is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally. Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The damage to your liver builds up over time. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. It lies up under your ribs on the right side of
Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Management of Thrombocytopenia in Chronic Liver Disease
251 Acute Liver Failure in Critical Care Anaesthesia UK
Improved medical management and the changing disease demographic mean that the majority of patients with chronic liver disease are living with the disease rather than dying from it.
Chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C represent about 8% of all cases of chronic liver disease in Australia. The rising prevalence of chronic liver disease contributes to increasing rates of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
Renal function is often impaired in chronic liver disease and may be an important factor to consider in drug management. The management strategy of any liver disease is a combination of treating the symptoms and complications that arise, as well as drug therapies relevant to …
Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Chronic disease management and optimal care
Management of Pruritus in Chronic Liver Disease
tions caused by chronic liver disease. Introduction Cirrhosis results in around 29,000 deaths annually in the United States. Patients with cirrhosis who do not receive a liver transplant have a 5-year mortality rate of up to 85%. Cirrhosis is the result of chronic inflamma-tion and development of fibrosis that leads to various complications of chronic liver disease. These complica-tions are
REVIEW ARTICLE Management of Thrombocytopenia in Chronic Liver Disease: Focus on Pharmacotherapeutic Strategies Raoel Maan1 • Robert J. de Knegt1 • Bart J. Veldt1
Liver has a central role in nutritional homeostasis and any liver disease leads to abnormalities in nutrient metabolism and subsequent malnutrition. All children with chronic liver disease (CLD) must undergo a periodic nutritional assessment — medical history, anthropometry esp. skinfold thickness
Diamond T, Stiel D, Mason R, Lissner D, Bikle D, Wilson S, Posen S. Serum vitamin D metabolites are not responsible for low turnover osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Dec; 69 (6):1234–1239.
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases. Edited by Anne M. Larson. Volume 98, Issue 1, Pages 1-180 (January 2014) Previous vol/issue. Next vol/issue. Select all documents. Download PDFs. Export. Show all article previews Show all article previews. select article CME Accreditation Page and Author Disclosures. Examination Full text access CME Accreditation Page and Author …
While chronic kidney disease (CKD), low albumin, and high Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)-Na score were found to be statistically significant predictors of morbidity. Addition of sepsis in conventional MELD score predicted mortality even better than MELD-Na (area under receiver operating characteristic: 0.735 vs 0.686; P 1.3 d. Evidence of encephalopathy e. Illness duration < 28 days d. Concerning the management of neurological complications in ALF: a. Target PaCO 2 is that of low-normal range b. Hypertonic saline is a recognised treatment for cerebral oedema c. All patients should have invasive intra-cranial pressure
Chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C represent about 8% of all cases of chronic liver disease in Australia. The rising prevalence of chronic liver disease contributes to increasing rates of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
Management of End-Stage Liver Disease in Chronic Hepatitis B Hui-Hui Tan, MBBS, MRCPa,*, Paul Martin, MD, FRCP, FRCPIb Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the most common cause of chronic …
therapies for patients with liver disease, liver biopsy and histological assessment of the liver has now taken on an important role in clinical management. Therefore, as of 2009, liver biopsy currently has three major roles: (1) for diagnosis, (2) for assessment of prognosis (disease stag-ing), and/or (3) to assist in making therapeutic manage-ment decisions. Diagnosis. For many diseases
Childhood liver disorders have, in general, mode of presentations which are distinct from that in adult population. It is due to varying etiology and natural history of the liver diseases in
A chronic disease management model for chronic liver
Value ofLiver Biopsy in the Evaluation and Management of
Absence of chronic liver disease b. Acute transaminitis (ALT/AST) c. Coagulopathy with INR > 1.3 d. Evidence of encephalopathy e. Illness duration < 28 days d. Concerning the management of neurological complications in ALF: a. Target PaCO 2 is that of low-normal range b. Hypertonic saline is a recognised treatment for cerebral oedema c. All patients should have invasive intra-cranial pressure
Chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C represent about 8% of all cases of chronic liver disease in Australia. The rising prevalence of chronic liver disease contributes to increasing rates of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
Cirrhosis is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally. Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The damage to your liver builds up over time. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. It lies up under your ribs on the right side of
Efficacy of a Chronic Disease Management Model for Patients With Chronic Liver Failure ALAN J. WIGG,* ROSEMARY MCCORMICK,* RACHEL WUNDKE,* and RICHARD J. WOODMAN‡
Relationships Between Nutrition, Alcohol Use, and Liver Disease Charles S. Lieber, M.D., M.A.C.P. Many alcoholics are malnourished, either because they ingest too
Plasma immunoreactive beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in chronic liver disease and fulminant hepatic failure. J Invest Dermatol 1978 ; 70 : 326 – 327 . Barton JC , McDonnell SM , Adams PC , et al. Management of hemochromatosis.
Liver Disease Management and Care of Patients 6KNIN337
Chronic disease management and optimal care
End Stage Liver Failure Aetiology of Chronic Liver Disease – Neonatal liver disease – Chronic hepatitis – Metabolic – Fibropolycystic liver disease
to download a pdf or request a hard copy. th 2 Forewor d This third edition of Chronic Kidney This third edition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice is the synthesis of the evolving evidence that the management of kidney disease matters. The Kidney Check Australia Task Force (KCAT) -now in its 13 year- has produced this book in the hope that practitioners will
Fluid and Electrolyte Management in Chronic Liver Disease Most patients with ascites caused by cirrhosis have an impaired renal handling of water that results in dilutional hyponatremia, the severity of which correlates directly with the severity of liver disease.
Download file Free Book PDF Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart at Complete PDF Library. This Book have some digital formats such us : paperbook, ebook, kindle, epub, and another formats. Here is The Complete PDF Book Library. It’s free to register here to get Book file PDF Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart. Decompensated alcohol related liver disease …
The effect that chronic liver disease has on a child’s nutritional status and health is determined by the cause and severity of the liver disease and the age of onset.
Conventional wisdom is that chronic liver disease is an acquired bleeding disorder. However, the imbalance between procoagulant and anticoagulant activities can also lead to thrombosis. Studies
Chronic Disease Management Schedule Checklist – a reminder summary of when to claim and schedule in best care for your chronic disease clients Putting the Patient in the Picture resource – general practice clinics including systems and data management, setting up and implementing the clinic, and self-management and prevention.
Cirrhosis is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally. Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The damage to your liver builds up over time. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. It lies up under your ribs on the right side of
Childhood liver disorders have, in general, mode of presentations which are distinct from that in adult population. It is due to varying etiology and natural history of the liver diseases in
of liver transplants, the clinical features of liver disease, and the medical and dental management of children before and after liver transplantation.(Pediatr Dent 21:273-281, 1999)
Efficacy of a Chronic Disease Management Model for Patients With Chronic Liver Failure ALAN J. WIGG,* ROSEMARY MCCORMICK,* RACHEL WUNDKE,* and RICHARD J. WOODMAN‡
7/8/2016 1 Ryan M. Ford, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Transplant Hepatology Director of Viral Hepatitis Emory Transplant Center 7. Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)
Managing the rising burden of chronic liver disease
Liver Disease Management and Care of Patients 6KNIN337
Childhood liver disorders have, in general, mode of presentations which are distinct from that in adult population. It is due to varying etiology and natural history of the liver diseases in
Improved medical management and the changing disease demographic mean that the majority of patients with chronic liver disease are living with the disease rather than dying from it.
Liver has a central role in nutritional homeostasis and any liver disease leads to abnormalities in nutrient metabolism and subsequent malnutrition. All children with chronic liver disease (CLD) must undergo a periodic nutritional assessment — medical history, anthropometry esp. skinfold thickness
associated with liver failure, (3) interpretation of biochemical test of liver disease and failure, (4) ancillary tests used in evaluation and management of equine liver failure, and (5) treatment and prognosis of liver failure.
The main complications of the patient with liver disease are risk of contagion (for healthcare personnel and other patients), the risk of bleeding and the risk of toxicity due …
Relationships Between Nutrition, Alcohol Use, and Liver Disease Charles S. Lieber, M.D., M.A.C.P. Many alcoholics are malnourished, either because they ingest too
chronic liver disease and hepatic and extrahepatic organ failures, and is associated with substantial short-term mortality. Common precipitants include bacterial and viral infections, alcoholic hepatitis, and surgery, but in more
REVIEW ARTICLE Management of Thrombocytopenia in Chronic Liver Disease: Focus on Pharmacotherapeutic Strategies Raoel Maan1 • Robert J. de Knegt1 • Bart J. Veldt1
Chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C represent about 8% of all cases of chronic liver disease in Australia. The rising prevalence of chronic liver disease contributes to increasing rates of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
Liver failure or hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic. [1]
Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Plasma immunoreactive beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in chronic liver disease and fulminant hepatic failure. J Invest Dermatol 1978 ; 70 : 326 – 327 . Barton JC , McDonnell SM , Adams PC , et al. Management of hemochromatosis.
to download a pdf or request a hard copy. th 2 Forewor d This third edition of Chronic Kidney This third edition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice is the synthesis of the evolving evidence that the management of kidney disease matters. The Kidney Check Australia Task Force (KCAT) -now in its 13 year- has produced this book in the hope that practitioners will
of liver transplants, the clinical features of liver disease, and the medical and dental management of children before and after liver transplantation.(Pediatr Dent 21:273-281, 1999)
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases
Evaluation and Management of Osteoporosis in Liver Disease
The main complications of the patient with liver disease are risk of contagion (for healthcare personnel and other patients), the risk of bleeding and the risk of toxicity due …
Liver failure or hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic. [1]
10/03/2015 · Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases. Edited by Anne M. Larson. Volume 98, Issue 1, Pages 1-180 (January 2014) Previous vol/issue. Next vol/issue. Select all documents. Download PDFs. Export. Show all article previews Show all article previews. select article CME Accreditation Page and Author Disclosures. Examination Full text access CME Accreditation Page and Author …
Childhood liver disorders have, in general, mode of presentations which are distinct from that in adult population. It is due to varying etiology and natural history of the liver diseases in
DIET AND NUTRITION FOR LIVER DISEASE AND HEPATITIS By Dr . Hassan El Shennawy Prof. of medicine National Liver Institute Menoufya Universty. Contents : Introduction DIET IN ACUTE LIVER DISEASE DIET IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE DIET AS A CAUSE OF LIVER DISEASE DRUG NUTRIENT INTERACTION. Questions frequently asked by liver diseased patient concerning diet …
Chronic cholestasis is a well-accepted risk factor for osteopenia [53 x [53] Collier, J.D., Ninkovic, M., and Compston, J.E. Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated with chronic liver disease.
Chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C represent about 8% of all cases of chronic liver disease in Australia. The rising prevalence of chronic liver disease contributes to increasing rates of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
Malnutrition in chronic liver disease is better defined as protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) because kwashiorkor- like malnutrition and marasmus frequently coexist (3, 4).
of liver transplants, the clinical features of liver disease, and the medical and dental management of children before and after liver transplantation.(Pediatr Dent 21:273-281, 1999)
associated with liver failure, (3) interpretation of biochemical test of liver disease and failure, (4) ancillary tests used in evaluation and management of equine liver failure, and (5) treatment and prognosis of liver failure.
The effect that chronic liver disease has on a child’s nutritional status and health is determined by the cause and severity of the liver disease and the age of onset.
Cirrhosis is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally. Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The damage to your liver builds up over time. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. It lies up under your ribs on the right side of
Chronic disease management and optimal care
SUPPLEMENT Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis
Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Efficacy of a Chronic Disease Management Model for Patients With Chronic Liver Failure ALAN J. WIGG,* ROSEMARY MCCORMICK,* RACHEL WUNDKE,* and RICHARD J. WOODMAN‡
liver disease, a joint single topic conference was recently sponsored by the Brazilian Society of Hepatology in cooperation with the Brazilian Society of Intensive Care Medicine and the Brazilian Association for Organ Transplantation.
Cirrhosis is when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally. Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The damage to your liver builds up over time. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. It lies up under your ribs on the right side of
Improved medical management and the changing disease demographic mean that the majority of patients with chronic liver disease are living with the disease rather than dying from it.
Diagnosis and management of bone disease in patients with chronic liver disease. *Calcium (1,000–1,500 mg/d) and 25(OH)D (400–800 IU/d or 260 µg every two weeks) to preserve normal levels. **According to the severity of liver disease and cholestasis, and in patients taking corticosteroids.
associated with liver failure, (3) interpretation of biochemical test of liver disease and failure, (4) ancillary tests used in evaluation and management of equine liver failure, and (5) treatment and prognosis of liver failure.
Chronic Disease Management Schedule Checklist – a reminder summary of when to claim and schedule in best care for your chronic disease clients Putting the Patient in the Picture resource – general practice clinics including systems and data management, setting up and implementing the clinic, and self-management and prevention.
End Stage Liver Failure Aetiology of Chronic Liver Disease – Neonatal liver disease – Chronic hepatitis – Metabolic – Fibropolycystic liver disease
Download file Free Book PDF Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart at Complete PDF Library. This Book have some digital formats such us : paperbook, ebook, kindle, epub, and another formats. Here is The Complete PDF Book Library. It’s free to register here to get Book file PDF Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart. Decompensated alcohol related liver disease …
The management of children with chronic liver disease (CLD) mandates a multidisciplinary approach. CLDs can be classified into ‘potentially’ curable, treatable non-curable, and end-stage diseases.
Fluid and Electrolyte Management in Chronic Liver Disease Most patients with ascites caused by cirrhosis have an impaired renal handling of water that results in dilutional hyponatremia, the severity of which correlates directly with the severity of liver disease.
therapies for patients with liver disease, liver biopsy and histological assessment of the liver has now taken on an important role in clinical management. Therefore, as of 2009, liver biopsy currently has three major roles: (1) for diagnosis, (2) for assessment of prognosis (disease stag-ing), and/or (3) to assist in making therapeutic manage-ment decisions. Diagnosis. For many diseases
Malnutrition in chronic liver disease is better defined as protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) because kwashiorkor- like malnutrition and marasmus frequently coexist (3, 4).
Chronic liver disease is increasingly prevalent and, as the population ages, geriatricians will see an increasing burden. We present an overview of the investigation and management of older adults with chronic parenchymal liver disease and highlight the potential roles of transjugular intrahepatic portosytemic shunts and orthotopic liver transplantation.
Dental management of children undergoing liver transplantation
The Coagulopathy of Chronic Liver Disease NEJM
Background. There continues to be uncertainty on the ideal treatment of pruritus in chronic liver disease. The aim of this study was to gather the latest information on the evidence-based management of pruritus in chronic liver disease.
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Liver Diseases. Edited by Anne M. Larson. Volume 98, Issue 1, Pages 1-180 (January 2014) Previous vol/issue. Next vol/issue. Select all documents. Download PDFs. Export. Show all article previews Show all article previews. select article CME Accreditation Page and Author Disclosures. Examination Full text access CME Accreditation Page and Author …
care management and the use of emergency liver transplantation.5 In this review, with chronic liver disease and often result from idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury or are indeterminate
Download file Free Book PDF Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart at Complete PDF Library. This Book have some digital formats such us : paperbook, ebook, kindle, epub, and another formats. Here is The Complete PDF Book Library. It’s free to register here to get Book file PDF Management Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Gordon Stuart. Decompensated alcohol related liver disease …
Liver has a central role in nutritional homeostasis and any liver disease leads to abnormalities in nutrient metabolism and subsequent malnutrition. All children with chronic liver disease (CLD) must undergo a periodic nutritional assessment — medical history, anthropometry esp. skinfold thickness
Liver failure or hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic. [1]
7/8/2016 1 Ryan M. Ford, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Transplant Hepatology Director of Viral Hepatitis Emory Transplant Center 7. Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)
with unexplained acute and chronic liver injury, as well as when prescribing certain gastrointestinal medications (e.g., azathio- prine, anti-tumor necrosis factor agents, sulfonamides) ( 7,8 ).
Conventional wisdom is that chronic liver disease is an acquired bleeding disorder. However, the imbalance between procoagulant and anticoagulant activities can also lead to thrombosis. Studies
The effect that chronic liver disease has on a child’s nutritional status and health is determined by the cause and severity of the liver disease and the age of onset.