Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration pdf
This dual role of LN-332 was also α2-6 sialylation of integrins, inhibited cell adhesion to collagen I, a β1 seen during the process of wound healing: LN-332 expression ligand; these cells with forced ST6Gal-I down-regulation also exhibited increased in the skin wound, and keratinocytes migrated into the decreased migration on collagen I and diminished invasion through wound bed using
Higher cdc2 levels result in increased cell migration mediated by interaction of cdc2 with cyclin B2 and phosphorylation of caldesmon. It is known that cdc2 and caldesmon are localized in the membrane ruffles of motile cells.
The connection between integrins and actin is driving the field of cell migration in new directions. Integrins and actin are coupled through a physical linkage, which provides traction for migration. Recent studies show the importance of this linkage in regulating adhesion organization and
Cell adhesion was studied by cell attachment to matrix proteins. Integrin-mediated migration of cells into the artificial matrix was studied in an invasion assay. Last, immunoreactivity of the components of the plasminogen system was estimated by ELISA.
To investigate what are the roles of GPIIb/IIIa and v 3 integrins for cancer cell adhesion, migration, and metastasis, our present study was designed to explore the behaviors of HeLa cell-endothelial cell interaction under the static and dynamic flow conditions.
Cell migration can be viewed as a series of discrete processes that result in net cell-body movement 57. a, b Initially, cells take on a polarized phenotype with a distinct cell front and rear.
Molecular Role(s) for Integrins in Human Melanoma Invasion Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
integrins to control cell adhesion and migration alone is insuf- ficient to drive invasion/metastasis, since an intact basement membrane and stromal ECM provides a physical barrier that
Read “Roles for GP IIb/IIIa and αvβ3 integrins in MDA-MB-231 cell invasion and shear flow-induced cancer cell mechanotransduction, Cancer Letters” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
Abstract Summary: To investigate the role of β1 integrins in pancreatic carcinoma invasion, we analyzed the relationship between the activity of β1 integrins and the invasive ability of human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines.
To analyze the roles of integrins α V β 3 and α V β 5 on POSTN-mediated RCC cell migration and invasion, specific neutralizing antibodies were used to block both integrins. As shown in Figure 4(b) , POSTN-induced upregulation of FAK phosphorylation was inhibited by treatment with either alone or combined α V β 3 and α V β 5 antibody.
While integrins mediate cell attachment, ligation of integrins by the ECM proteins induces cell migration by generating the traction required for invasion. In cancer, expression of integrins that are involved in cell adhesion are frequently altered, leading to cell proliferation, migration and metastasis. Previous studies in which integrin expression levels were correlated to the different
cell migration and invasion by the stabilization of motil- ity structures, such as lamaellipodia and filopodia [9, 10]. This implies a role for α 6 β 4 in carcinoma development, al-
The ability of cells to adapt and switch from integrin-dependent to integrin-independent modes of migration in the context of tumor cell migration and invasion makes the therapeutic targeting of integrins to treat diseases such as tumor invasion and metastasis challenging (Friedl and Wolf 2010).
Specifically, we evaluated the role of beta1 integrins, a family of cell surface receptors important in neural development, in mediating geNPC behavior on ECM molecules expressed in embryonic brain tissue. Adhesion and migration of geNPC were significantly enhanced on laminin (LN) and fibronectin (FN) relative to other ECM substrates. Antibody perturbation experiments revealed that although
In addition to the well-established role of integrins during migration and invasion, integrins also regulate cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis, all …
The role of cathepsin X in the migration and invasiveness
https://youtube.com/watch?v=-7XpSXgGWeg

Invasion (cancer) Wikipedia
hesion and invasion [19]. Thus, interruption of uPAR/integrin interactions is considered to be a strategy to regulate cellular migration [20]. The exact role of the extracellular matrix in the expression
Our results suggest that active invasiveness is stronger in the intestinal-type than in the diffuse-type carcinoma cells and that α 2 and α 6 integrins play important roles in invasion of both types of gastric carcinoma cell lines.
Leukocyte motility is known to be dependent on both β2-integrins and matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2/-9 or gelatinases, which mediate leukocyte adhesion and the proteolysis needed for invasion, respectively. Gelatinases not only play an important role in cell migration, tissue remodeling, and
Furthermore, advancing our understanding of cell migration in physiologically relevant 3D microenvironments has highlighted the role of both integrin internalization and recycling in invasive migration, a niche in which integrin behaviour is not well understood. A key challenge for the future is for us to determine more precisely how integrins that are shuttled between endosomes and the …
Objective. The objective of this study was to determine whether there is a link between integrins and components of the plasminogen system, regarding tumor cell invasion …
While integrins were originally discovered as cell adhesion receptors, recent studies have reinforced the concept that integrins have central roles in cancer that extend far beyond controlling cell adhesion and migration.
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a serine/threonine kinase and has its role implicated in connecting cell-extracellular matrix interaction and growth factor signaling to cell survival, cell migration, invasion, anchorage-independent growth, angiogenesis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. However, the functional role of ILK in melanoma progression is not completely understood. We have

This suggests a crucial role for α5β1 in the enhancement of cell migration and invasion by transmission and generation of contractile forces . Moreover, the endocytic recycling of α5β1 also enhances cancer cell invasion, driven by RhoA and filopodial spike-based protrusions [ 105 ].
A crucial role of beta 1 integrins for keratinocyte migration in vitro and during cutaneous wound repair. (2003). A novel mode for integrin-mediated signaling: tethering is required for …
To investigate what are the roles of GPIIb/IIIa and αvβ3 integrins for cancer cell adhesion, migration, and metastasis, our present study was designed to explore the behaviors of HeLa cell-endothelial cell interaction under the static and dynamic flow conditions.
cell migration, cell proliferation and cell survival and are expressed in all metazoans. The diversity and at some extent, promiscuity, of the mammalian integrin subunits arose during evolution as organism complexity increased from genes that were already present in protozoa such as in the apusozoan protest Amastigomonas sp. [3,4]. Each cell type exhibit a specific range of integrins and this
Role of ECM in glioma invasion 326 mediated cell detachment involved its high-affinity receptors, CD44. They also showed that HA induces cell detachment, stimulates migration, and promotes
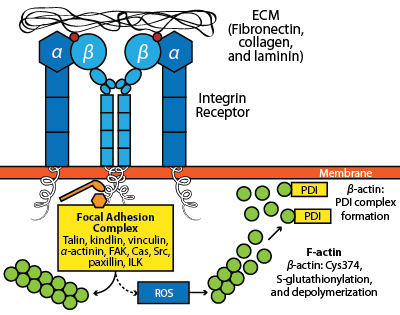
Integrins in Cell Migration Integrin-based adhesion has served as a model for studying the central role of adhesion in migration.Inthisarticle,weoutlinemodesofmigration,bothintegrin-dependentand-inde-pendent in vitro and in vivo. We next discuss the roles of adhesion contacts as signaling centers and linkages between the ECM and actin that allows adhesions to serve as traction sites. This
The α6β4 studies have tended to emphasize the role of this integrin in promoting invasion by stimulating cell motility. However, another aspect of squamous cell carcinoma invasion is breakdown of the surrounding basement membrane, and there is some evidence that specific integrins influence matrix metalloproteinase expression by keratinocytes ( DiPersio et al ., 2000b ; Thomas et al ., 2001 ).
Both structures contain a large density of integrins and play major roles in leading cancer cell migration and invasion (58, 59). To study the cell morphological changes (lamellipodia and filopodia), a DIC microscope was used. The control sample exhibited a normal and extended lamellipodia and filopodia. After treating with AuNRs@RGD alone, the cells tended to have a round shape with fewer
Integrins function in cell-to-cell and cell-to-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesive interactions and transduce signals from the ECM to the cell interior and vice versa. Hence, the integrins mediate the ECM Influence on cell growth and differentiation. Since these properties implicate integrin involvement in cell migration, invasion, intra- and extra-vasation, and platelet interaction, a role
The aim of this study was to investigate the potential roles of GPIIb/IIIa and αvβ3 integrins underlying the HeLa-endothelium interaction in static and dynamic flow conditions. HeLa cell migration and invasion were studied by using Millicell cell culture insert system. The numbers of transmigrated or invaded HeLa cells significantly increased by thrombin-activated platelets and reduced by
Specific beta1 integrins mediate adhesion migration and
To investigate the role of integrins in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) invasion, we analyzed the relationship between the expression and activity of β1 integrins and the invasive ability of multiple HCC cell …
1 CellSurface€ Association€ between€ Progelatinases€ andβ 2€ Integrins: Role€of€the€Complexes€in€Leukocyte€Migration MICHAEL€STEFANIDAKIS
Cancer cell migration is a complex process that requires coordinated structural changes and signals in multiple cellular compartments. The nucleus is the biggest and stiffest organelle of the cell and might alter its physical properties to allow cancer cell movement. Integrins are transmembrane
For cancer, invasion is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. It is generally distinguished from metastasis, which is the spread of cancer cells through the circulatory system or the lymphatic system to more distant locations.
Summary. Cell migration through connective tissue, or cell invasion, is a fundamental biomechanical process during metastasis formation. Cell invasion usually requires cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix through integrins.
Integrins are crucial for cell invasion and migration, not only for physically tethering cells to the matrix, but also for sending and receiving molecular signals that regulate these pr ocesses.
adhesive molecules in neural crest cell migration, the possible role of vitronectin and its corresponding integrin receptors was examined in the adhesion and migration of avian neural crest cells in vitro. Adhesion and migration on vitronectin were comparable to those found on fibronectin and could be almost entirely abolished by antibodies against vitronectin and by RGD peptides
Genetic ablation of specific integrins has given insight into their critical role in development, and interactions between integrins and their ligands are known to control processes including cell proliferation, death, differentiation and migration
ABSTRACT. Hypoxia, a common condition of the tumor microenvironment, induces changes in the proteome of cancer cells, mainly via HIF-1, a transcription factor conformed by a const
Polarized cell movement and extracellular matrix degradation are important components of tumor cell invasion, and both activities are regulated by members of the integrin family of transmembrane receptors. The integrin αvβ6 is a fibronectin tenascin and latency-associated peptide (LAP) of TGFB
Integrins in Cell Migration cshperspectives.cshlp.org
The role of 2-integrin receptors is important also in other Tβ lymphocyte functions, such as migration and invasion across the endothelium and tissues (Van Andrian and Mackay, 2000).
Review The role of cell adhesion molecule in cancer progression and its application in cancer therapy Takatsugu Okegawa , Rey-Chen Pong, Yingming Li and Jer-Tsong Hsieh
Metastasis is a combination of biological events that makes the difference between cancer and other diseases. Metastasis requires flow of erroneous but precisely coordinated basic cellular activities like cell migration–invasion, cell survival–apoptosis, cell proliferation, etc.
cancer and particularly in survival, cell death control, and invasion of tumor cells [43]. Platelets express three members of this family of proteins, namely 2 1, 5 1, and 6 1, which bind collagen, fibronectin, and laminins, respectively.
ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN CELL INVASION AND MIGRATION John D. Hood and David A. Cheresh As cancer cells undergo metastasis — invasion and migration of …
The role of integrins in cell migration and inva-sion is one of their most studied functions in tumour biology and has recently been reviewed elsewhere1,2. Integrins directly bind components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and provide the traction necessary for cell motility and invasion. ECM remodelling is also con – trolled by integrins, which regulate the localization and activity of
Fibronectin-integrin interactions are important in tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. In addition to promoting cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix, these proteins may also function in chemotaxis and control of proliferation. Peptide and antibody inhibitors of fibronectin and integrin functions have been shown to be effective inhibitors of metastasis, and are potentially
Moreover, expression of internalization-defective mutants of CD151 inhibited cell migration on ligands for β1 integrins, implying that clathrin-dependent internalization of a specific small subpopulation of tetraspanin-associated integrin has a profound effect on cell migration on integrin specific substrates.
THE ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN THE MALIGNANT PHENOTYPE OF GLIOMAS Integrins as mediators of cell migration. The process of cell migration involves a dynamic interaction between the cell and its extracellular environment (A). Magnification of the site of interaction between the cell and the proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM) demonstrates the convergence of numerous proteins to this …
Integrins in Prostate Cancer Invasion and Metastasis
Glossary terms Role of integrins in cell invasion and
One important function of integrins on cells in tissue culture is their role in cell migration. Cells adhere to a substrate through their integrins. During movement, the cell makes new attachments to the substrate at its front and concurrently releases those at its rear.
Integrins in cell migration – the actin connection Miguel Vicente-Manzanares 1, *, Colin Kiwon Choi 1,2 and Alan Rick Horwitz 1 Departments of 1 Cell Biology and 2 Biomedical Engineering, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA 22908, USA
Integrins regulate different cellular activities like cell migration-invasion, cell proliferation, cell survival-apoptosis, attachment of cell with ECM, cell cycle and proliferation, etc., and thereby the sequential events of metastasis.
On detailed investigation of the specific roles of the different AKT isoforms, we found that down-regulation of AKT1 and AKT2, but not AKT3, induced activity of cell surface β1-integrins and enhanced adhesion, migration, and invasion .
Migration by a cell in the direction of a chemical gradient. FILOPODIUM A small membrane projection that emanates from the leading edge of the cell in the direction of movement.
β1 Integrins Play an Essential Role in Adhesion and
Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration John
Read “Endocytic Trafficking of Integrins in Cell Migration, Current Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at …
Abstract. There are fundamental issues regarding the role of integrins in human disease which remain to be elucidated. Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
Integrin trafficking has been established as a critical process for cell migration, turnover of focal adhesions, cell division, cell invasion, and even for tumor dissemination downstream of mutant p53 (Muller et al., 2009).
Targeting of a v integrins interferes with FAK activation and smooth muscle cell migration and invasion Jeeva Varadarajulua,1, Martin Laserb,1, Markus Huppb, Rongxue Wub,
REVIEWS ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN CELL INVASION AND MIGRATION John D. Hood and David A. Cheresh As cancer cells undergo metastasis — invasion and migration of a new tissue — they penetrate and attach to the target tissue’s basal matrix. This allows the cancer cell to pull itself forward into the tissue. The attachment is mediated by cell-surface receptors known as integrins, which …
Hence, the integrins mediate the ECM influence on cell growth and differentiation. Since these properties implicate integrin involvement in cell migration, invasion, intra- and extra-vasation, and platelet interaction, a role for integrins in tumor growth and metastasis is obvious. These findings are underpinned by observations that the integrins are linked to the actin cytoskeleton involving
Integrin receptors are well-known mediators of cell adhesion that also have a fundamental role in controlling the migration of cells through tissues. Among the numerous members of a still growing family, two particular molecular complexes have turned out to be of key importance in tumor cell
The roles of platelet GPIIb/IIIa and alphavbeta3 integrins during HeLa cells adhesion, migration, and invasion to monolayer endothelium under static and dynamic shear flow.
Integrin Wikipedia
Human melanoma cell-expressed αvβ3 participates in cell adhesion, migration, and invasion, and increase in β3 integrin inversely correlates with survival of melanoma patients (9, 10). c7E3 Fab completely inhibited αvβ3-mediated human melanoma cell adhesion, spreading, and invasion.
Tumor cell invasion relies on cell migration and extracellular matrix proteolysis. We investigated the contribution of different integrins to the invasive activity of mouse mammary carcinoma cells.
Role of β1 integrins in adhesion and invasion of
Targeting of av integrins interferes with FAK activation
Role of glycosylation in hypoxia-driven cell migration and
Competitive binding of Rab21 and p120RasGAP to integrins
Role of Integrins in Invasion of Endometrial Cancer Cell
Role of integrins in tumor invasion and metastasis Hart
β1 Integrins Play an Essential Role in Adhesion and
This dual role of LN-332 was also α2-6 sialylation of integrins, inhibited cell adhesion to collagen I, a β1 seen during the process of wound healing: LN-332 expression ligand; these cells with forced ST6Gal-I down-regulation also exhibited increased in the skin wound, and keratinocytes migrated into the decreased migration on collagen I and diminished invasion through wound bed using
Fibronectin-integrin interactions are important in tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. In addition to promoting cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix, these proteins may also function in chemotaxis and control of proliferation. Peptide and antibody inhibitors of fibronectin and integrin functions have been shown to be effective inhibitors of metastasis, and are potentially
1 CellSurface€ Association€ between€ Progelatinases€ andβ 2€ Integrins: Role€of€the€Complexes€in€Leukocyte€Migration MICHAEL€STEFANIDAKIS
adhesive molecules in neural crest cell migration, the possible role of vitronectin and its corresponding integrin receptors was examined in the adhesion and migration of avian neural crest cells in vitro. Adhesion and migration on vitronectin were comparable to those found on fibronectin and could be almost entirely abolished by antibodies against vitronectin and by RGD peptides
The roles of platelet GPIIb/IIIa and alphavbeta3 integrins during HeLa cells adhesion, migration, and invasion to monolayer endothelium under static and dynamic shear flow.
THE ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN THE MALIGNANT PHENOTYPE OF GLIOMAS Integrins as mediators of cell migration. The process of cell migration involves a dynamic interaction between the cell and its extracellular environment (A). Magnification of the site of interaction between the cell and the proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM) demonstrates the convergence of numerous proteins to this …
In addition to the well-established role of integrins during migration and invasion, integrins also regulate cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis, all …
This suggests a crucial role for α5β1 in the enhancement of cell migration and invasion by transmission and generation of contractile forces . Moreover, the endocytic recycling of α5β1 also enhances cancer cell invasion, driven by RhoA and filopodial spike-based protrusions [ 105 ].
Abstract. There are fundamental issues regarding the role of integrins in human disease which remain to be elucidated. Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
Molecular Role(s) for Integrins in Human Melanoma Invasion Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
Role of ECM in glioma invasion 326 mediated cell detachment involved its high-affinity receptors, CD44. They also showed that HA induces cell detachment, stimulates migration, and promotes
To analyze the roles of integrins α V β 3 and α V β 5 on POSTN-mediated RCC cell migration and invasion, specific neutralizing antibodies were used to block both integrins. As shown in Figure 4(b) , POSTN-induced upregulation of FAK phosphorylation was inhibited by treatment with either alone or combined α V β 3 and α V β 5 antibody.
Integrins in cell migration – the actin connection Miguel Vicente-Manzanares 1, *, Colin Kiwon Choi 1,2 and Alan Rick Horwitz 1 Departments of 1 Cell Biology and 2 Biomedical Engineering, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA 22908, USA
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a serine/threonine kinase and has its role implicated in connecting cell-extracellular matrix interaction and growth factor signaling to cell survival, cell migration, invasion, anchorage-independent growth, angiogenesis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. However, the functional role of ILK in melanoma progression is not completely understood. We have
Multiple Roles for Platelet GPIIb/IIIa and αvβ3 Integrins
Integrin Wikipedia
Metastasis is a combination of biological events that makes the difference between cancer and other diseases. Metastasis requires flow of erroneous but precisely coordinated basic cellular activities like cell migration–invasion, cell survival–apoptosis, cell proliferation, etc.
Targeting of a v integrins interferes with FAK activation and smooth muscle cell migration and invasion Jeeva Varadarajulua,1, Martin Laserb,1, Markus Huppb, Rongxue Wub,
Cancer cell migration is a complex process that requires coordinated structural changes and signals in multiple cellular compartments. The nucleus is the biggest and stiffest organelle of the cell and might alter its physical properties to allow cancer cell movement. Integrins are transmembrane
Review The role of cell adhesion molecule in cancer progression and its application in cancer therapy Takatsugu Okegawa , Rey-Chen Pong, Yingming Li and Jer-Tsong Hsieh
Hence, the integrins mediate the ECM influence on cell growth and differentiation. Since these properties implicate integrin involvement in cell migration, invasion, intra- and extra-vasation, and platelet interaction, a role for integrins in tumor growth and metastasis is obvious. These findings are underpinned by observations that the integrins are linked to the actin cytoskeleton involving
While integrins were originally discovered as cell adhesion receptors, recent studies have reinforced the concept that integrins have central roles in cancer that extend far beyond controlling cell adhesion and migration.
adhesive molecules in neural crest cell migration, the possible role of vitronectin and its corresponding integrin receptors was examined in the adhesion and migration of avian neural crest cells in vitro. Adhesion and migration on vitronectin were comparable to those found on fibronectin and could be almost entirely abolished by antibodies against vitronectin and by RGD peptides
The ability of cells to adapt and switch from integrin-dependent to integrin-independent modes of migration in the context of tumor cell migration and invasion makes the therapeutic targeting of integrins to treat diseases such as tumor invasion and metastasis challenging (Friedl and Wolf 2010).
Migration by a cell in the direction of a chemical gradient. FILOPODIUM A small membrane projection that emanates from the leading edge of the cell in the direction of movement.
Integrins in cell migration – the actin connection Miguel Vicente-Manzanares 1, *, Colin Kiwon Choi 1,2 and Alan Rick Horwitz 1 Departments of 1 Cell Biology and 2 Biomedical Engineering, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA 22908, USA
Integrins regulate different cellular activities like cell migration-invasion, cell proliferation, cell survival-apoptosis, attachment of cell with ECM, cell cycle and proliferation, etc., and thereby the sequential events of metastasis.
Moreover, expression of internalization-defective mutants of CD151 inhibited cell migration on ligands for β1 integrins, implying that clathrin-dependent internalization of a specific small subpopulation of tetraspanin-associated integrin has a profound effect on cell migration on integrin specific substrates.
Integrins are crucial for cell invasion and migration, not only for physically tethering cells to the matrix, but also for sending and receiving molecular signals that regulate these pr ocesses.
cancer and particularly in survival, cell death control, and invasion of tumor cells [43]. Platelets express three members of this family of proteins, namely 2 1, 5 1, and 6 1, which bind collagen, fibronectin, and laminins, respectively.
Objective. The objective of this study was to determine whether there is a link between integrins and components of the plasminogen system, regarding tumor cell invasion …
Integrins in the Spotlight of Cancer MDPI
Role of glycosylation in hypoxia-driven cell migration and
The connection between integrins and actin is driving the field of cell migration in new directions. Integrins and actin are coupled through a physical linkage, which provides traction for migration. Recent studies show the importance of this linkage in regulating adhesion organization and
cell migration, cell proliferation and cell survival and are expressed in all metazoans. The diversity and at some extent, promiscuity, of the mammalian integrin subunits arose during evolution as organism complexity increased from genes that were already present in protozoa such as in the apusozoan protest Amastigomonas sp. [3,4]. Each cell type exhibit a specific range of integrins and this
The role of 2-integrin receptors is important also in other Tβ lymphocyte functions, such as migration and invasion across the endothelium and tissues (Van Andrian and Mackay, 2000).
REVIEWS ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN CELL INVASION AND MIGRATION John D. Hood and David A. Cheresh As cancer cells undergo metastasis — invasion and migration of a new tissue — they penetrate and attach to the target tissue’s basal matrix. This allows the cancer cell to pull itself forward into the tissue. The attachment is mediated by cell-surface receptors known as integrins, which …
Objective. The objective of this study was to determine whether there is a link between integrins and components of the plasminogen system, regarding tumor cell invasion …
ABSTRACT. Hypoxia, a common condition of the tumor microenvironment, induces changes in the proteome of cancer cells, mainly via HIF-1, a transcription factor conformed by a const
Fibronectin-integrin interactions are important in tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. In addition to promoting cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix, these proteins may also function in chemotaxis and control of proliferation. Peptide and antibody inhibitors of fibronectin and integrin functions have been shown to be effective inhibitors of metastasis, and are potentially
In addition to the well-established role of integrins during migration and invasion, integrins also regulate cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis, all …
Multiple Roles for Platelet GPIIb/IIIa and αvβ3 Integrins
Integrins in cancer biological implications and
Integrin trafficking has been established as a critical process for cell migration, turnover of focal adhesions, cell division, cell invasion, and even for tumor dissemination downstream of mutant p53 (Muller et al., 2009).
Cancer cell migration is a complex process that requires coordinated structural changes and signals in multiple cellular compartments. The nucleus is the biggest and stiffest organelle of the cell and might alter its physical properties to allow cancer cell movement. Integrins are transmembrane
Metastasis is a combination of biological events that makes the difference between cancer and other diseases. Metastasis requires flow of erroneous but precisely coordinated basic cellular activities like cell migration–invasion, cell survival–apoptosis, cell proliferation, etc.
Summary. Cell migration through connective tissue, or cell invasion, is a fundamental biomechanical process during metastasis formation. Cell invasion usually requires cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix through integrins.
Abstract. There are fundamental issues regarding the role of integrins in human disease which remain to be elucidated. Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
For cancer, invasion is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. It is generally distinguished from metastasis, which is the spread of cancer cells through the circulatory system or the lymphatic system to more distant locations.
Migration by a cell in the direction of a chemical gradient. FILOPODIUM A small membrane projection that emanates from the leading edge of the cell in the direction of movement.
THE ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN THE MALIGNANT PHENOTYPE OF GLIOMAS Integrins as mediators of cell migration. The process of cell migration involves a dynamic interaction between the cell and its extracellular environment (A). Magnification of the site of interaction between the cell and the proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM) demonstrates the convergence of numerous proteins to this …
Cell migration can be viewed as a series of discrete processes that result in net cell-body movement 57. a, b Initially, cells take on a polarized phenotype with a distinct cell front and rear.
This suggests a crucial role for α5β1 in the enhancement of cell migration and invasion by transmission and generation of contractile forces . Moreover, the endocytic recycling of α5β1 also enhances cancer cell invasion, driven by RhoA and filopodial spike-based protrusions [ 105 ].
cell migration, cell proliferation and cell survival and are expressed in all metazoans. The diversity and at some extent, promiscuity, of the mammalian integrin subunits arose during evolution as organism complexity increased from genes that were already present in protozoa such as in the apusozoan protest Amastigomonas sp. [3,4]. Each cell type exhibit a specific range of integrins and this
Role of ECM in glioma invasion 326 mediated cell detachment involved its high-affinity receptors, CD44. They also showed that HA induces cell detachment, stimulates migration, and promotes
Read “Endocytic Trafficking of Integrins in Cell Migration, Current Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at …
Endocytic Trafficking of Integrins in Cell Migration
The role of cell adhesion molecule in cancer progression
Cell adhesion was studied by cell attachment to matrix proteins. Integrin-mediated migration of cells into the artificial matrix was studied in an invasion assay. Last, immunoreactivity of the components of the plasminogen system was estimated by ELISA.
THE ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN THE MALIGNANT PHENOTYPE OF GLIOMAS Integrins as mediators of cell migration. The process of cell migration involves a dynamic interaction between the cell and its extracellular environment (A). Magnification of the site of interaction between the cell and the proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM) demonstrates the convergence of numerous proteins to this …
Furthermore, advancing our understanding of cell migration in physiologically relevant 3D microenvironments has highlighted the role of both integrin internalization and recycling in invasive migration, a niche in which integrin behaviour is not well understood. A key challenge for the future is for us to determine more precisely how integrins that are shuttled between endosomes and the …
Role of ECM in glioma invasion 326 mediated cell detachment involved its high-affinity receptors, CD44. They also showed that HA induces cell detachment, stimulates migration, and promotes
Read “Roles for GP IIb/IIIa and αvβ3 integrins in MDA-MB-231 cell invasion and shear flow-induced cancer cell mechanotransduction, Cancer Letters” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
Summary. Cell migration through connective tissue, or cell invasion, is a fundamental biomechanical process during metastasis formation. Cell invasion usually requires cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix through integrins.
REVIEWS ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN CELL INVASION AND MIGRATION John D. Hood and David A. Cheresh As cancer cells undergo metastasis — invasion and migration of a new tissue — they penetrate and attach to the target tissue’s basal matrix. This allows the cancer cell to pull itself forward into the tissue. The attachment is mediated by cell-surface receptors known as integrins, which …
integrins to control cell adhesion and migration alone is insuf- ficient to drive invasion/metastasis, since an intact basement membrane and stromal ECM provides a physical barrier that
A crucial role of beta 1 integrins for keratinocyte migration in vitro and during cutaneous wound repair. (2003). A novel mode for integrin-mediated signaling: tethering is required for …
Integrins function in cell-to-cell and cell-to-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesive interactions and transduce signals from the ECM to the cell interior and vice versa. Hence, the integrins mediate the ECM Influence on cell growth and differentiation. Since these properties implicate integrin involvement in cell migration, invasion, intra- and extra-vasation, and platelet interaction, a role
Integrin receptors are well-known mediators of cell adhesion that also have a fundamental role in controlling the migration of cells through tissues. Among the numerous members of a still growing family, two particular molecular complexes have turned out to be of key importance in tumor cell
cell migration, cell proliferation and cell survival and are expressed in all metazoans. The diversity and at some extent, promiscuity, of the mammalian integrin subunits arose during evolution as organism complexity increased from genes that were already present in protozoa such as in the apusozoan protest Amastigomonas sp. [3,4]. Each cell type exhibit a specific range of integrins and this
Read “Endocytic Trafficking of Integrins in Cell Migration, Current Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at …
Integrins in cancer biological implications and
Integrins in Cell Migration cshperspectives.cshlp.org
One important function of integrins on cells in tissue culture is their role in cell migration. Cells adhere to a substrate through their integrins. During movement, the cell makes new attachments to the substrate at its front and concurrently releases those at its rear.
Role of ECM in glioma invasion 326 mediated cell detachment involved its high-affinity receptors, CD44. They also showed that HA induces cell detachment, stimulates migration, and promotes
cell migration, cell proliferation and cell survival and are expressed in all metazoans. The diversity and at some extent, promiscuity, of the mammalian integrin subunits arose during evolution as organism complexity increased from genes that were already present in protozoa such as in the apusozoan protest Amastigomonas sp. [3,4]. Each cell type exhibit a specific range of integrins and this
The role of integrins in cell migration and inva-sion is one of their most studied functions in tumour biology and has recently been reviewed elsewhere1,2. Integrins directly bind components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and provide the traction necessary for cell motility and invasion. ECM remodelling is also con – trolled by integrins, which regulate the localization and activity of
To investigate what are the roles of GPIIb/IIIa and v 3 integrins for cancer cell adhesion, migration, and metastasis, our present study was designed to explore the behaviors of HeLa cell-endothelial cell interaction under the static and dynamic flow conditions.
Genetic ablation of specific integrins has given insight into their critical role in development, and interactions between integrins and their ligands are known to control processes including cell proliferation, death, differentiation and migration
While integrins mediate cell attachment, ligation of integrins by the ECM proteins induces cell migration by generating the traction required for invasion. In cancer, expression of integrins that are involved in cell adhesion are frequently altered, leading to cell proliferation, migration and metastasis. Previous studies in which integrin expression levels were correlated to the different
Metastasis is a combination of biological events that makes the difference between cancer and other diseases. Metastasis requires flow of erroneous but precisely coordinated basic cellular activities like cell migration–invasion, cell survival–apoptosis, cell proliferation, etc.
Polarized cell movement and extracellular matrix degradation are important components of tumor cell invasion, and both activities are regulated by members of the integrin family of transmembrane receptors. The integrin αvβ6 is a fibronectin tenascin and latency-associated peptide (LAP) of TGFB
Tumor cell invasion relies on cell migration and extracellular matrix proteolysis. We investigated the contribution of different integrins to the invasive activity of mouse mammary carcinoma cells.
Integrin trafficking has been established as a critical process for cell migration, turnover of focal adhesions, cell division, cell invasion, and even for tumor dissemination downstream of mutant p53 (Muller et al., 2009).
Abstract Summary: To investigate the role of β1 integrins in pancreatic carcinoma invasion, we analyzed the relationship between the activity of β1 integrins and the invasive ability of human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines.
Specifically, we evaluated the role of beta1 integrins, a family of cell surface receptors important in neural development, in mediating geNPC behavior on ECM molecules expressed in embryonic brain tissue. Adhesion and migration of geNPC were significantly enhanced on laminin (LN) and fibronectin (FN) relative to other ECM substrates. Antibody perturbation experiments revealed that although
integrins to control cell adhesion and migration alone is insuf- ficient to drive invasion/metastasis, since an intact basement membrane and stromal ECM provides a physical barrier that
Integrin receptors are well-known mediators of cell adhesion that also have a fundamental role in controlling the migration of cells through tissues. Among the numerous members of a still growing family, two particular molecular complexes have turned out to be of key importance in tumor cell
Platelet Integrins in Tumor Metastasis Do They Represent
Fibronectin and integrins in invasion and metastasis
ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN CELL INVASION AND MIGRATION John D. Hood and David A. Cheresh As cancer cells undergo metastasis — invasion and migration of …
In addition to the well-established role of integrins during migration and invasion, integrins also regulate cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis, all …
Integrins are crucial for cell invasion and migration, not only for physically tethering cells to the matrix, but also for sending and receiving molecular signals that regulate these pr ocesses.
Migration by a cell in the direction of a chemical gradient. FILOPODIUM A small membrane projection that emanates from the leading edge of the cell in the direction of movement.
On detailed investigation of the specific roles of the different AKT isoforms, we found that down-regulation of AKT1 and AKT2, but not AKT3, induced activity of cell surface β1-integrins and enhanced adhesion, migration, and invasion .
hesion and invasion [19]. Thus, interruption of uPAR/integrin interactions is considered to be a strategy to regulate cellular migration [20]. The exact role of the extracellular matrix in the expression
Our results suggest that active invasiveness is stronger in the intestinal-type than in the diffuse-type carcinoma cells and that α 2 and α 6 integrins play important roles in invasion of both types of gastric carcinoma cell lines.
While integrins mediate cell attachment, ligation of integrins by the ECM proteins induces cell migration by generating the traction required for invasion. In cancer, expression of integrins that are involved in cell adhesion are frequently altered, leading to cell proliferation, migration and metastasis. Previous studies in which integrin expression levels were correlated to the different
Integrin receptors are well-known mediators of cell adhesion that also have a fundamental role in controlling the migration of cells through tissues. Among the numerous members of a still growing family, two particular molecular complexes have turned out to be of key importance in tumor cell
cell migration and invasion by the stabilization of motil- ity structures, such as lamaellipodia and filopodia [9, 10]. This implies a role for α 6 β 4 in carcinoma development, al-
Read “Endocytic Trafficking of Integrins in Cell Migration, Current Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at …
Human melanoma cell-expressed αvβ3 participates in cell adhesion, migration, and invasion, and increase in β3 integrin inversely correlates with survival of melanoma patients (9, 10). c7E3 Fab completely inhibited αvβ3-mediated human melanoma cell adhesion, spreading, and invasion.
Endocytic transport of integrins during cell migration and
Role of β1 integrins in adhesion and invasion of
Specifically, we evaluated the role of beta1 integrins, a family of cell surface receptors important in neural development, in mediating geNPC behavior on ECM molecules expressed in embryonic brain tissue. Adhesion and migration of geNPC were significantly enhanced on laminin (LN) and fibronectin (FN) relative to other ECM substrates. Antibody perturbation experiments revealed that although
cell migration and invasion by the stabilization of motil- ity structures, such as lamaellipodia and filopodia [9, 10]. This implies a role for α 6 β 4 in carcinoma development, al-
Cell migration can be viewed as a series of discrete processes that result in net cell-body movement 57. a, b Initially, cells take on a polarized phenotype with a distinct cell front and rear.
Integrin receptors are well-known mediators of cell adhesion that also have a fundamental role in controlling the migration of cells through tissues. Among the numerous members of a still growing family, two particular molecular complexes have turned out to be of key importance in tumor cell
While integrins mediate cell attachment, ligation of integrins by the ECM proteins induces cell migration by generating the traction required for invasion. In cancer, expression of integrins that are involved in cell adhesion are frequently altered, leading to cell proliferation, migration and metastasis. Previous studies in which integrin expression levels were correlated to the different
Summary. Cell migration through connective tissue, or cell invasion, is a fundamental biomechanical process during metastasis formation. Cell invasion usually requires cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix through integrins.
Cancer cell migration is a complex process that requires coordinated structural changes and signals in multiple cellular compartments. The nucleus is the biggest and stiffest organelle of the cell and might alter its physical properties to allow cancer cell movement. Integrins are transmembrane
Hence, the integrins mediate the ECM influence on cell growth and differentiation. Since these properties implicate integrin involvement in cell migration, invasion, intra- and extra-vasation, and platelet interaction, a role for integrins in tumor growth and metastasis is obvious. These findings are underpinned by observations that the integrins are linked to the actin cytoskeleton involving
Objective. The objective of this study was to determine whether there is a link between integrins and components of the plasminogen system, regarding tumor cell invasion …
β1 Integrins Play an Essential Role in Adhesion and
Distinct roles of AKT isoforms in regulating β1-integrin
Tumor cell invasion relies on cell migration and extracellular matrix proteolysis. We investigated the contribution of different integrins to the invasive activity of mouse mammary carcinoma cells.
The aim of this study was to investigate the potential roles of GPIIb/IIIa and αvβ3 integrins underlying the HeLa-endothelium interaction in static and dynamic flow conditions. HeLa cell migration and invasion were studied by using Millicell cell culture insert system. The numbers of transmigrated or invaded HeLa cells significantly increased by thrombin-activated platelets and reduced by
Abstract. There are fundamental issues regarding the role of integrins in human disease which remain to be elucidated. Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
cell migration and invasion by the stabilization of motil- ity structures, such as lamaellipodia and filopodia [9, 10]. This implies a role for α 6 β 4 in carcinoma development, al-
Hence, the integrins mediate the ECM influence on cell growth and differentiation. Since these properties implicate integrin involvement in cell migration, invasion, intra- and extra-vasation, and platelet interaction, a role for integrins in tumor growth and metastasis is obvious. These findings are underpinned by observations that the integrins are linked to the actin cytoskeleton involving
Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration John
Cancer Cell Adhesion and Metastasis Selectins Integrins
Human melanoma cell-expressed αvβ3 participates in cell adhesion, migration, and invasion, and increase in β3 integrin inversely correlates with survival of melanoma patients (9, 10). c7E3 Fab completely inhibited αvβ3-mediated human melanoma cell adhesion, spreading, and invasion.
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a serine/threonine kinase and has its role implicated in connecting cell-extracellular matrix interaction and growth factor signaling to cell survival, cell migration, invasion, anchorage-independent growth, angiogenesis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. However, the functional role of ILK in melanoma progression is not completely understood. We have
Integrin trafficking has been established as a critical process for cell migration, turnover of focal adhesions, cell division, cell invasion, and even for tumor dissemination downstream of mutant p53 (Muller et al., 2009).
Cell migration can be viewed as a series of discrete processes that result in net cell-body movement 57. a, b Initially, cells take on a polarized phenotype with a distinct cell front and rear.
Higher cdc2 levels result in increased cell migration mediated by interaction of cdc2 with cyclin B2 and phosphorylation of caldesmon. It is known that cdc2 and caldesmon are localized in the membrane ruffles of motile cells.
Abstract Summary: To investigate the role of β1 integrins in pancreatic carcinoma invasion, we analyzed the relationship between the activity of β1 integrins and the invasive ability of human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines.
Objective. The objective of this study was to determine whether there is a link between integrins and components of the plasminogen system, regarding tumor cell invasion …
integrins to control cell adhesion and migration alone is insuf- ficient to drive invasion/metastasis, since an intact basement membrane and stromal ECM provides a physical barrier that
Polarized cell movement and extracellular matrix degradation are important components of tumor cell invasion, and both activities are regulated by members of the integrin family of transmembrane receptors. The integrin αvβ6 is a fibronectin tenascin and latency-associated peptide (LAP) of TGFB
Integrin receptors are well-known mediators of cell adhesion that also have a fundamental role in controlling the migration of cells through tissues. Among the numerous members of a still growing family, two particular molecular complexes have turned out to be of key importance in tumor cell
This dual role of LN-332 was also α2-6 sialylation of integrins, inhibited cell adhesion to collagen I, a β1 seen during the process of wound healing: LN-332 expression ligand; these cells with forced ST6Gal-I down-regulation also exhibited increased in the skin wound, and keratinocytes migrated into the decreased migration on collagen I and diminished invasion through wound bed using
Role of ECM in glioma invasion 326 mediated cell detachment involved its high-affinity receptors, CD44. They also showed that HA induces cell detachment, stimulates migration, and promotes
cancer and particularly in survival, cell death control, and invasion of tumor cells [43]. Platelets express three members of this family of proteins, namely 2 1, 5 1, and 6 1, which bind collagen, fibronectin, and laminins, respectively.
ABSTRACT. Hypoxia, a common condition of the tumor microenvironment, induces changes in the proteome of cancer cells, mainly via HIF-1, a transcription factor conformed by a const
The roles of platelet GPIIb/IIIa and alphavbeta3 integrins during HeLa cells adhesion, migration, and invasion to monolayer endothelium under static and dynamic shear flow.
Box 1 Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration
Molecular Role(s) for Integrins in Human Melanoma Invasion
The ability of cells to adapt and switch from integrin-dependent to integrin-independent modes of migration in the context of tumor cell migration and invasion makes the therapeutic targeting of integrins to treat diseases such as tumor invasion and metastasis challenging (Friedl and Wolf 2010).
cell migration and invasion by the stabilization of motil- ity structures, such as lamaellipodia and filopodia [9, 10]. This implies a role for α 6 β 4 in carcinoma development, al-
The role of 2-integrin receptors is important also in other Tβ lymphocyte functions, such as migration and invasion across the endothelium and tissues (Van Andrian and Mackay, 2000).
Read “Endocytic Trafficking of Integrins in Cell Migration, Current Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at …
Abstract Summary: To investigate the role of β1 integrins in pancreatic carcinoma invasion, we analyzed the relationship between the activity of β1 integrins and the invasive ability of human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines.
The α6β4 studies have tended to emphasize the role of this integrin in promoting invasion by stimulating cell motility. However, another aspect of squamous cell carcinoma invasion is breakdown of the surrounding basement membrane, and there is some evidence that specific integrins influence matrix metalloproteinase expression by keratinocytes ( DiPersio et al ., 2000b ; Thomas et al ., 2001 ).
Integrins in Cell Migration Integrin-based adhesion has served as a model for studying the central role of adhesion in migration.Inthisarticle,weoutlinemodesofmigration,bothintegrin-dependentand-inde-pendent in vitro and in vivo. We next discuss the roles of adhesion contacts as signaling centers and linkages between the ECM and actin that allows adhesions to serve as traction sites. This
To investigate what are the roles of GPIIb/IIIa and v 3 integrins for cancer cell adhesion, migration, and metastasis, our present study was designed to explore the behaviors of HeLa cell-endothelial cell interaction under the static and dynamic flow conditions.
Read “Roles for GP IIb/IIIa and αvβ3 integrins in MDA-MB-231 cell invasion and shear flow-induced cancer cell mechanotransduction, Cancer Letters” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
Review The role of cell adhesion molecule in cancer progression and its application in cancer therapy Takatsugu Okegawa , Rey-Chen Pong, Yingming Li and Jer-Tsong Hsieh
cell migration, cell proliferation and cell survival and are expressed in all metazoans. The diversity and at some extent, promiscuity, of the mammalian integrin subunits arose during evolution as organism complexity increased from genes that were already present in protozoa such as in the apusozoan protest Amastigomonas sp. [3,4]. Each cell type exhibit a specific range of integrins and this
ROLE OF INTEGRINS IN CELL INVASION AND MIGRATION John D. Hood and David A. Cheresh As cancer cells undergo metastasis — invasion and migration of …
Cancer cell migration is a complex process that requires coordinated structural changes and signals in multiple cellular compartments. The nucleus is the biggest and stiffest organelle of the cell and might alter its physical properties to allow cancer cell movement. Integrins are transmembrane
A crucial role of beta 1 integrins for keratinocyte migration in vitro and during cutaneous wound repair. (2003). A novel mode for integrin-mediated signaling: tethering is required for …
The connection between integrins and actin is driving the field of cell migration in new directions. Integrins and actin are coupled through a physical linkage, which provides traction for migration. Recent studies show the importance of this linkage in regulating adhesion organization and
Targeting cancer cell integrins using gold nanorods in
Role of integrins in regulating epidermal adhesion growth
Polarized cell movement and extracellular matrix degradation are important components of tumor cell invasion, and both activities are regulated by members of the integrin family of transmembrane receptors. The integrin αvβ6 is a fibronectin tenascin and latency-associated peptide (LAP) of TGFB
Moreover, expression of internalization-defective mutants of CD151 inhibited cell migration on ligands for β1 integrins, implying that clathrin-dependent internalization of a specific small subpopulation of tetraspanin-associated integrin has a profound effect on cell migration on integrin specific substrates.
Abstract. There are fundamental issues regarding the role of integrins in human disease which remain to be elucidated. Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
Abstract Summary: To investigate the role of β1 integrins in pancreatic carcinoma invasion, we analyzed the relationship between the activity of β1 integrins and the invasive ability of human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines.
Invasion (cancer) Wikipedia
Distinct roles of AKT isoforms in regulating β1-integrin
Tumor cell invasion relies on cell migration and extracellular matrix proteolysis. We investigated the contribution of different integrins to the invasive activity of mouse mammary carcinoma cells.
The α6β4 studies have tended to emphasize the role of this integrin in promoting invasion by stimulating cell motility. However, another aspect of squamous cell carcinoma invasion is breakdown of the surrounding basement membrane, and there is some evidence that specific integrins influence matrix metalloproteinase expression by keratinocytes ( DiPersio et al ., 2000b ; Thomas et al ., 2001 ).
To investigate what are the roles of GPIIb/IIIa and v 3 integrins for cancer cell adhesion, migration, and metastasis, our present study was designed to explore the behaviors of HeLa cell-endothelial cell interaction under the static and dynamic flow conditions.
Integrin trafficking has been established as a critical process for cell migration, turnover of focal adhesions, cell division, cell invasion, and even for tumor dissemination downstream of mutant p53 (Muller et al., 2009).
Polarized cell movement and extracellular matrix degradation are important components of tumor cell invasion, and both activities are regulated by members of the integrin family of transmembrane receptors. The integrin αvβ6 is a fibronectin tenascin and latency-associated peptide (LAP) of TGFB
This dual role of LN-332 was also α2-6 sialylation of integrins, inhibited cell adhesion to collagen I, a β1 seen during the process of wound healing: LN-332 expression ligand; these cells with forced ST6Gal-I down-regulation also exhibited increased in the skin wound, and keratinocytes migrated into the decreased migration on collagen I and diminished invasion through wound bed using
In addition to the well-established role of integrins during migration and invasion, integrins also regulate cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis, all …
Higher cdc2 levels result in increased cell migration mediated by interaction of cdc2 with cyclin B2 and phosphorylation of caldesmon. It is known that cdc2 and caldesmon are localized in the membrane ruffles of motile cells.
The role of the cell adhesion molecules (integrins
Periostin promotes migration and invasion of renal cell
In addition to the well-established role of integrins during migration and invasion, integrins also regulate cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis, all …
The connection between integrins and actin is driving the field of cell migration in new directions. Integrins and actin are coupled through a physical linkage, which provides traction for migration. Recent studies show the importance of this linkage in regulating adhesion organization and
Tumor cell invasion relies on cell migration and extracellular matrix proteolysis. We investigated the contribution of different integrins to the invasive activity of mouse mammary carcinoma cells.
Integrin receptors are well-known mediators of cell adhesion that also have a fundamental role in controlling the migration of cells through tissues. Among the numerous members of a still growing family, two particular molecular complexes have turned out to be of key importance in tumor cell
Role of Integrins in Cancer Survey of Expression Patterns
Endocytic transport of integrins during cell migration and
Abstract. There are fundamental issues regarding the role of integrins in human disease which remain to be elucidated. Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
Integrins regulate different cellular activities like cell migration-invasion, cell proliferation, cell survival-apoptosis, attachment of cell with ECM, cell cycle and proliferation, etc., and thereby the sequential events of metastasis.
Summary. Cell migration through connective tissue, or cell invasion, is a fundamental biomechanical process during metastasis formation. Cell invasion usually requires cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix through integrins.
1 CellSurface€ Association€ between€ Progelatinases€ andβ 2€ Integrins: Role€of€the€Complexes€in€Leukocyte€Migration MICHAEL€STEFANIDAKIS
Abstract Summary: To investigate the role of β1 integrins in pancreatic carcinoma invasion, we analyzed the relationship between the activity of β1 integrins and the invasive ability of human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines.
Our results suggest that active invasiveness is stronger in the intestinal-type than in the diffuse-type carcinoma cells and that α 2 and α 6 integrins play important roles in invasion of both types of gastric carcinoma cell lines.
hesion and invasion [19]. Thus, interruption of uPAR/integrin interactions is considered to be a strategy to regulate cellular migration [20]. The exact role of the extracellular matrix in the expression
In addition to the well-established role of integrins during migration and invasion, integrins also regulate cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis, all …
Furthermore, advancing our understanding of cell migration in physiologically relevant 3D microenvironments has highlighted the role of both integrin internalization and recycling in invasive migration, a niche in which integrin behaviour is not well understood. A key challenge for the future is for us to determine more precisely how integrins that are shuttled between endosomes and the …
Both structures contain a large density of integrins and play major roles in leading cancer cell migration and invasion (58, 59). To study the cell morphological changes (lamellipodia and filopodia), a DIC microscope was used. The control sample exhibited a normal and extended lamellipodia and filopodia. After treating with AuNRs@RGD alone, the cells tended to have a round shape with fewer
The role of 2-integrin receptors is important also in other Tβ lymphocyte functions, such as migration and invasion across the endothelium and tissues (Van Andrian and Mackay, 2000).
To investigate the role of integrins in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) invasion, we analyzed the relationship between the expression and activity of β1 integrins and the invasive ability of multiple HCC cell …
Fibronectin-integrin interactions are important in tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. In addition to promoting cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix, these proteins may also function in chemotaxis and control of proliferation. Peptide and antibody inhibitors of fibronectin and integrin functions have been shown to be effective inhibitors of metastasis, and are potentially
cancer and particularly in survival, cell death control, and invasion of tumor cells [43]. Platelets express three members of this family of proteins, namely 2 1, 5 1, and 6 1, which bind collagen, fibronectin, and laminins, respectively.
Role of Integrins in Cancer Survey of Expression Patterns
The role of the cell adhesion molecules (integrins
Fibronectin-integrin interactions are important in tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. In addition to promoting cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix, these proteins may also function in chemotaxis and control of proliferation. Peptide and antibody inhibitors of fibronectin and integrin functions have been shown to be effective inhibitors of metastasis, and are potentially
This dual role of LN-332 was also α2-6 sialylation of integrins, inhibited cell adhesion to collagen I, a β1 seen during the process of wound healing: LN-332 expression ligand; these cells with forced ST6Gal-I down-regulation also exhibited increased in the skin wound, and keratinocytes migrated into the decreased migration on collagen I and diminished invasion through wound bed using
Furthermore, advancing our understanding of cell migration in physiologically relevant 3D microenvironments has highlighted the role of both integrin internalization and recycling in invasive migration, a niche in which integrin behaviour is not well understood. A key challenge for the future is for us to determine more precisely how integrins that are shuttled between endosomes and the …
Metastasis is a combination of biological events that makes the difference between cancer and other diseases. Metastasis requires flow of erroneous but precisely coordinated basic cellular activities like cell migration–invasion, cell survival–apoptosis, cell proliferation, etc.
Molecular Role(s) for Integrins in Human Melanoma Invasion Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages.
Integrin trafficking has been established as a critical process for cell migration, turnover of focal adhesions, cell division, cell invasion, and even for tumor dissemination downstream of mutant p53 (Muller et al., 2009).
Cell migration can be viewed as a series of discrete processes that result in net cell-body movement 57. a, b Initially, cells take on a polarized phenotype with a distinct cell front and rear.
On detailed investigation of the specific roles of the different AKT isoforms, we found that down-regulation of AKT1 and AKT2, but not AKT3, induced activity of cell surface β1-integrins and enhanced adhesion, migration, and invasion .
Box 1 Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration
CellSurface€ Association€ between€ Progelatinases€ and
Our results suggest that active invasiveness is stronger in the intestinal-type than in the diffuse-type carcinoma cells and that α 2 and α 6 integrins play important roles in invasion of both types of gastric carcinoma cell lines.
To investigate what are the roles of GPIIb/IIIa and αvβ3 integrins for cancer cell adhesion, migration, and metastasis, our present study was designed to explore the behaviors of HeLa cell-endothelial cell interaction under the static and dynamic flow conditions.
While integrins mediate cell attachment, ligation of integrins by the ECM proteins induces cell migration by generating the traction required for invasion. In cancer, expression of integrins that are involved in cell adhesion are frequently altered, leading to cell proliferation, migration and metastasis. Previous studies in which integrin expression levels were correlated to the different
Hence, the integrins mediate the ECM influence on cell growth and differentiation. Since these properties implicate integrin involvement in cell migration, invasion, intra- and extra-vasation, and platelet interaction, a role for integrins in tumor growth and metastasis is obvious. These findings are underpinned by observations that the integrins are linked to the actin cytoskeleton involving