Vygotsky cognitive development theory pdf
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
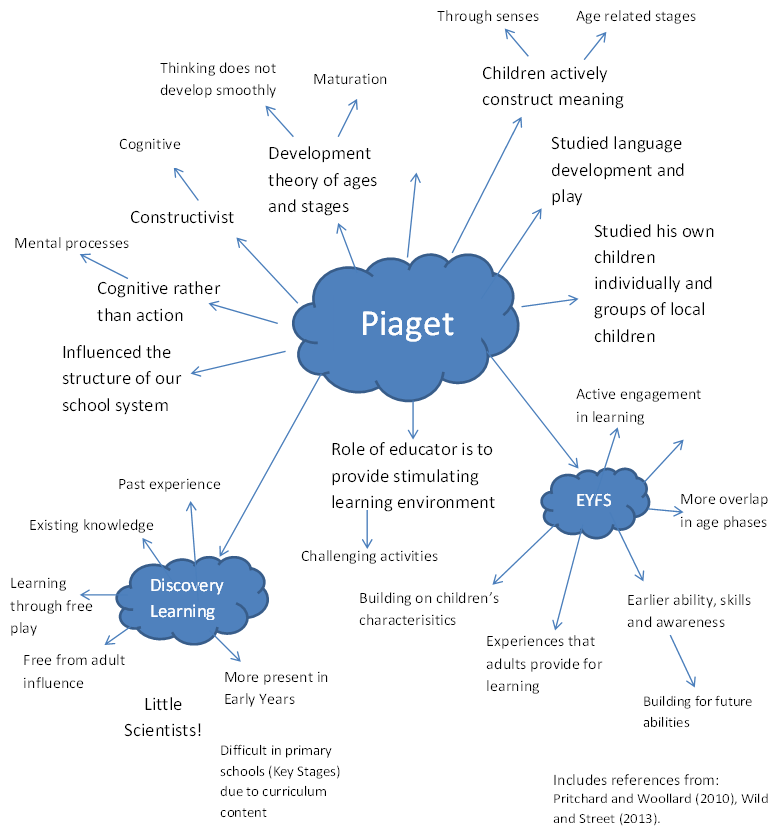
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
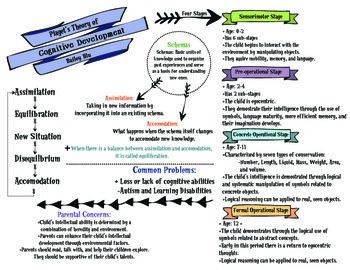
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
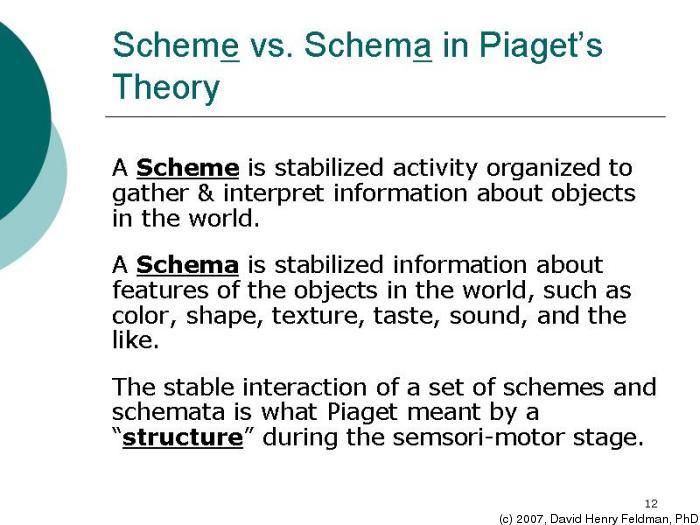
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LdSZV0Knwiw
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LRnCQ_9qnL4
https://youtube.com/watch?v=IhcgYgx7aAA
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LdSZV0Knwiw

https://youtube.com/watch?v=-p_-0n2f35o
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
Chapter 11 The Preschooler: Basic Assessment and Health Promotion 359 knowledge, languages, problem-solving tactics, and memory strategies (97). Thereby cognitive development differs between
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
tural perspective, cognitive development is embedded in social contexts and their separation is considered impossible and, thus, cannot have ‘e!ectsa. Like Smith, we claim that there is an overlooked similarity between Piaget and Vygotsky. However, from a recent sociocultural perspective, we associate these similarities with a shared failure to recognize the unity of cognition and social
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
Constructivism is a philosophical viewpoint about the nature of knowledge. Specifically, it represents an ontological stance. There are many flavors of constructivism, but one prominent theorist is Jean Piaget, who focused on how humans make meaning in relation …
Cognitive development is the term used to describe the construction of thought process, including remembering, problem solving and decision-making, from childhood through adolescence to adulthood.
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Montero, forthcoming), Vygotsky claimed that the development of verbal mediation is evidenced in children’s use of self-directed language (now commonly known as private speech) to accompany and regulate their behavior.
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
1 1 Children’s Cognitive Development: Alternatives to Piaget Steve Croker / Room C009 / Ext. 2081 s.croker@derby.ac.uk Outline: Brief review of Piaget’s theory
Piaget _ Cognitive Theory. pdf. changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed his children’s thinking as Definition: The first stage in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, during this through the development and refinement of schemas.
Vygotsky developed a sociocultural approach to cognitive development but he died at the age of 38 and so his theories are incomplete – although some of his …
VYGOTSKY’S THEORY OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Whereas Piaget had a background in biology, Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) had early training in law, history, philosophy, literature, and education.
Theories of Cognitive Development ‘cognitive’ theory • infant cognition • language development • conceptual development • mathematical and scientific reasoning • moral development . Piaget’s Most Revolutionary Idea Child as scientist 1. construct their own knowledge from experimenting on the world. 2. learn many things on their own without the intervention of older children
26 Applying Piaget’s Theory Applying Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development to Mathematics Instruction Bobby Ojose This paper is based on a presentation given at National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2005 in Anaheim, California. It explicates the developmental stages of the child as posited by Piaget. The author then ties each of the stages to developmentally appropriate
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.

Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, described in the next section, is an example of qualitative, discontinuous change in children’s thinking abilities.
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
A Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was the author of the theory of cognitive development called “the sociocultural theory.” Lev Vygotsky studied the mental development of children, including how they play and speak. He also studied the …
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Learning leads cognitive development Lev S. Vygotsky. The social formation of mind Vygotsky believed that individual development could not be understood without reference to the social and cultural context within which such development is embedded. Mind evolution is continuous Unlike Piaget or Bruner, Vygotsky focused on the mechanism of the development, excluding distinguishable …
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Another important difference between the two theories was that while Piaget’s theory suggests that development is largely universal, Vygotsky suggested that cognitive development can differ between different cultures. The course of development in a Western culture, for example, might be different than it is in an Eastern culture.
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF
2 COGNITIVE Pearson
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory of Learning Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist. He is considered as the father of social constructivist theory. He followed the work of John Piaget – who is attributed as the roots of constructivism1. While Piaget focused on stages of child development and individual construction of knowledge, Vygotsky identified the greater socio
Vygotsky’s Theory in the Classroom Introduction Request PDF