Laser beam machining process pdf
PDPM IIITDM JABALPUR LASER Beam Machining Advancements ME 306 ADVANCED MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Submitted To Dr. TVK Gupta Submitted By: …
Modern Machining UNIT 5 MODERN MACHINING METHOD Method 5.3 Non-conventional Machining Processes 5.4 Electrical Discharge Machining 5.5 Wire Cut Electric Discharge Machining 5.6 Ultrasonic Machining 5.7 Chemical Machining Processes 5.8 Electrochemical Machining 5.9 Laser Beam Machining 5.10 Plasma Arc Machining 5.11 Summary 5.12 Answers to SAQs 5.1 INTRODUCTION Modern machining …
The Advantages of AWJM Compared with other Machining Processes A. Advantages of AWJM compared with Lasers Beam Machining (LBM) Laser cutting involves using a laser focused on material to melt, burn, or vaporize the material. The laser can be a gas laser (such as CO2) or a solid-state laser. The laser beam can be static, and the material moves infront of the laser, or the laser …
Liquid Assisted Laser Beam Micromachining (LA-LBMM) process is advanced machining process which can overcome the limitations of traditional laser beam machining processes. LA-LBMM process uses a layer of a liquid medium such as water above the substrate surface during the application of laser beam
The polarization, reflection, absorption and trasmission of laser beam has practical meaning in laser machining processes and were discussed in section 2.8, 2.9. Besides common industrial lasers introduced in level 1, excimer lasers, semiconductor lasers are reviewed.
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter Optimization www.ijirst.org
3 Figure 2 Figure 2 depicts the process of metal spinning which Kryton performs on eight CNC machines. A disk of metal is rotated at high speed while a forming tool applies force to the disk.
Laser beam machining (LBM) is one of the most widely used thermal energy based non-contact type advance machining process which can be applied for almost whole range of materials.
significance of various laser beam machining processes on Inconel alloys and also a brief study has been done on the effects of various element composition on the Inconel properties. An overview of research works on Inconel alloys using laser beam
This slide contains the working process of Laser, their types and how they are used for machining purposes. Contents Laser Beam Machining Laser Type of Laser Laser Application Parameters Affecting LBM Advantage Disadvantage References 2 3. What is Laser LASER is the acronym for Light Amplified Stimulated Emission of Radiation Laser is a device which generates or amplifies light …
beam machining process uses highly coherent light source. beam can be focused by means of a lens on a very small spot in the work piece. This high power radiation of laser gives rise to high temperature on a small area of work piece.
Welding . Cladding . Alloying . Laser Beam welding. LBW is a versatile process, capable of welding carbon steels, HSLA steels, stainless steel, aluminum,
and Laser Welding & Cutting Tim Morris Technical Sales Manager TRUMPF Inc., Laser Technology Center. Agenda 1. Basics of lasers 2. Basics of laser welding 3. Summary. Flexibility … > beam manipulation (beam switching and sharing) > variety of product geometries and materials > ease of back-up (especially YAG) Often faster than other techniques > high power density weld process > …
A high energy-density laser beam vaporises the workpiece during the welding process to form a hole (keyhole), which allows the laser beam to penetrate into the metal to produce a deep, narrow melt pool.
Laser Drilling an overview ScienceDirect Topics
https://youtube.com/watch?v=FVFYBrAgqzQ
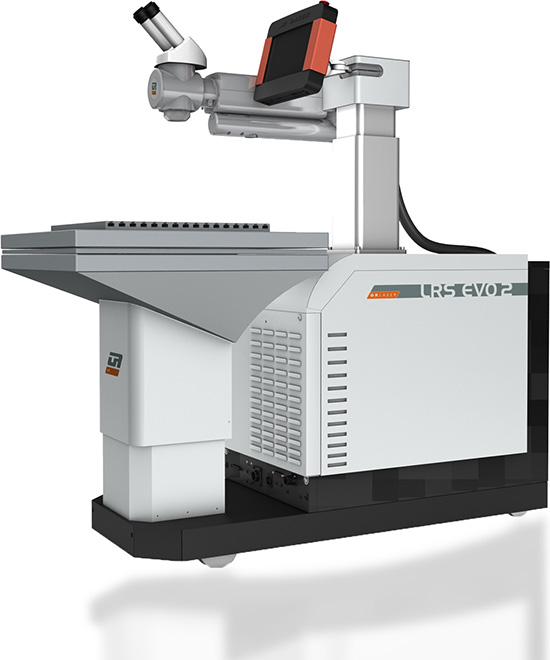

PDPM IIITDM JABALPUR WordPress.com
Today we have learned about Laser Beam Machining-Principle, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Application of Laser Beam Machining. If I have missed something, kindly inform me through commenting. If you
Laser beam machining (LBM) is one of the advanced machining processes which are used for shaping almost whole range of engineering materials. In LBM, surface roughness is one of important response which affects the quality characteristics of product. In this research work, the effect of process parameters such as cutting speed, frequency and duty cycle on surface roughness (Ra) for …
Electron Beam Machining (EBM) is a thermal process. Here a steam of high speed electrons impinges on the work surface so that the kinetic energy of electrons is …

Multi-objective Optimization of Laser Beam Machining Process Parameters 259 The experimental set up used for data collection is as given below: Machine
ME 677: Laser Material Processing Instructor: Ramesh Singh Laser Soldering and Brazing •In the laser soldering and brazing processes, the beam is used to melt a filler addition,
machining process at all. Laser beam machining is the machining processes involving a laser beam as a heat source. It is a thermal process used to remove materials without mechanical engagement with workpiece material where the workpiece is heated to melting or boiling point and removed by melt ejection, vaporization, or ablation mechanisms. In contrast with a conventional …
LBM is nontraditional thermal process. In thermal removing processes, thermal energy, provided by a heat source, melts or vaporizes the volume of the material to be removed. Among thermal removal methods, Electrical discharge machining or EDM is the oldest and most widely used. Electron-beam (EBM) and laser beam machining (LBM) are newer thermal techniques also widely accepted in …
Processes require transfer of energy from the laser beam to the work piece. Cutting process essentially consists of removing material. Laser cutting is done with the assistance of air, oxygen or dry nitrogen gas jet. The role of the jet is to cool the surface of the material and blow away the debris from the cutting zone. An arrangement for a gas-laser cutter. Advantages Laser cutting is
process parameters and performance characteristics For modeling and optimization of laser beam machining mostly taguchi method is used, but this methods will not provide an
Laser Beam Machining (LBM) is thermal processes considering the mechanisms of material removal. This in turn results in melting and vaporisation of the work material and finally material removal. Laser Beam Machining or more broadly laser material processing deals with machining and material processing like heat treatment. .
An overview is given of the state of the art of laser beam machining in general with special emphasis on applications of short and ultrashort lasers. In laser welding the trend is to apply optical sensors for process …
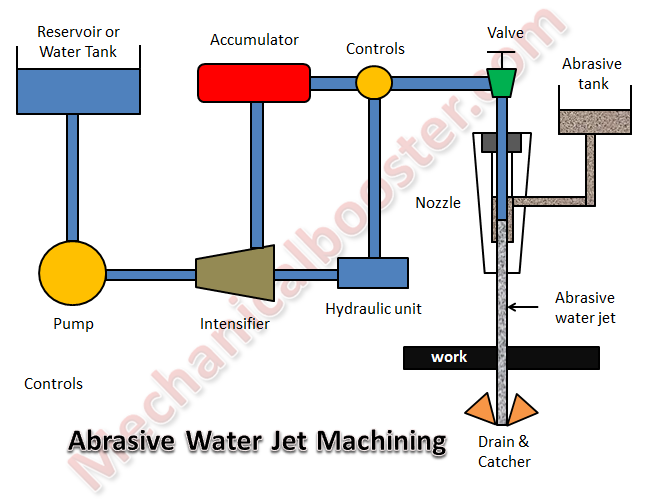
industries such as beam machining process (laser beam machining, electron beam machining, plasma beam machining), electro discharge machining, ultrasonic machining, electro chemical machining, jet machining processes (water jet machining, abrasive jet
Machining Economics
Laser Beam Machining – The Lasing Process • Lasing process describes the basic operation of laser, i.e. generation of coherent beam of light by
A method for laser beam machining of a workpiece in which a laser beam is focused by an objective, into or onto the workpiece having a boundary surface, to produce a machining effect by a two-photon process, and the position of the focal point with respect to the workpiece is shifted.
This chapter introduces two nontraditional machining processes: laser machining and electron beam machining (EBM). These two machining processes use laser and electron beams as energy sources to introduce thermal energy to remove work material by melting and/or vaporization.
Laser Micro-machining The laser beam is characterized by the half divergence angle θ micromachining process is one on a different time scale. Miliseconds 1×10-3 second Microseconds 1×10-6 second Nanoseconds 1×10-9 second Picoseconds 1×10-12 second Femtoseconds 1×10-15 second In other words, a femtosecond is a million times shorter than a nanosecond. Femtosecond …
Applications of laser beam machining cutcnccam.com
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Finite element analysis and simulation of liquid-assisted laser beam machining process Vinit Mistry 1 & Sagil James1 Received: 18 April 2017/Accepted: 17 August 2017/Published online: 7 September 2017
The adaptability of laser beam machining allows them to perform more than one function, and the wide range of industries that often use laser beam machining technology includes automakers and jewelers.
Thermal cutting processes differ from mechanical cutting (machining) in that the cutting action is initiated either by chemical reaction (oxidation) or melting (heat from arc).
Laser Beam Machining an overview ScienceDirect Topics

Laser beam machining CORE
https://youtube.com/watch?v=lpUYiYqMBew
2/02/2013 · I’ve just added a PDF file to the Knowledge Base to accompany my LBM (Laser Beam Machining) guide. It’s a 1 page overview covering the basics of the process.
beam machining (LBM) processes [ ]. e LBM, which is a thermal energy-based machining process, is now being widely applied to ful ll the present day requirements of high
Laser-beam machining is a thermal material-removal process that utilizes a high-energy, coherent light beam to melt and vaporize particles on the surface of metallic and non-metallic work pieces. Lasers can be used to cut, drill, weld and mark. LBM is particularly suitable for making accurately placed holes.
promoting their femtosecond laser machining processes. Figure 1: Chirped pulse amplification (CPA); how to build an ultra-short laser pulse. As with most new technologies, the first femtosecond lasers were expensive and often unreliable.
Laser beam machining (LBM) is a widely used thermal advance machining process capable of high accuracy machining of almost any material with complex geometries.
A method for laser beam machining, in particular laser beam welding of bodywork components (14), with the aid of a remote laser head (3). The laser head is guided by a …
Laser Beam Machining. Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. . Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. . Author Information
LASER CUTTING: FROM FIRST PRINCIPLES TO THE STATE OF THE ART Dr J. Powell1 and Dr A. Kaplan2 laser beam as shown in fig 1. (N.B. With certain materials this gas jet can accelerate the cutting process by doing chemical as well as physical work. For example, Carbon or mild steels are generally cut in a jet of pure oxygen. The oxidation process initiated by the laser heating generates …
Laser drilling is a process of removing solid material by irradiating it with a pulsed laser beam. The depth over which the amount of material ca ne removed in a single laser pulse depends mainly on the optical properties of the material and the laser wavelength. This process utilizes focused and pulsed UV-light to drill holes into the wafers. Consecutive sequences of laser pulses are focused
Several types of laser in manufacturing operation on Table
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter IJIRST
Laser Beam Machining or more broadly laser material processing deals with machining and material processing like heat treatment. the energy of the photon is absorbed by the work material leading to rapid substantial rise in local temperature. alloying. sheet metal bending. This in turn results in melting and vaporisation of the work material and finally material removal.
Abstract— Laser beam forming, a non-contact manufacturing process has become a viable manufacturing process for shaping metallic components.
Laser beam machining is a form of non-traditional machining that can machine almost any known materials. It is It is thermal, non-contact process, which does …
Laser cutting is a thermal separation process. Our pulsed Nd: YAG and fiber lasers permit a controlled heat entry which is optimum for fine cutting. The high peak performance of our laser permits a maximum cut depth of up to 10mm. As the laser beam can be focused on a very small diameter for high precision, fine cuts are possible with a minimum cut width of up to 15 µm (0.0006 in). In
Nd:YAG laser beam machining (LBM) process has a great potential to manufacture intricate shaped microproducts with its unique characteristics. In practical applications, such as drilling, grooving, cutting, or scribing, the optimal combination of Nd:YAG LBM process parameters needs to …
Electron-Beam Machining Process Figure 27.15 Schematic illustration of the electron-beam machining process. Unlike LBM, this process requires a vacuum, so workpiece size is limited to the size of the vacuum chamber.
In laser beam machining, the main concern is the machining quality as kerf width of the end product. It is essential for industrial It is essential for industrial applications to …
The cost of cutting hard-to-machine materials by conventional mechanical machining processes is high due to the low material removal rate and short tool life, and some materials are not possible to be cut by the conventional machining process at all. Laser beam machining is the machining processes
Laser Beam Machining. Laser beam machining (LBM) is a thermal energy based advanced machining process in which the material is removed by (i) melting, (ii) vaporization, and (iii) chemical degradation (chemical bonds are broken which causes the materials to degrade).
Laser Beam Machining-Working Principle Advantages
Lesson 40 Electron Beam and Laser Beam Machining Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur

laser_beam_machining Laser Sheet Metal
Laser beam machining—A review Request PDF
Laser Beam Machining Knowles – – Major Reference Works

LASER BEAM MACHINING OF INCONEL ALLOYS A REVIEW
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Uj2LkNcoRoQ
Experimental Investigation and Analysis of Process
laser_beam_machining Laser Sheet Metal
Laser Beam Machining pt.scribd.com
Liquid Assisted Laser Beam Micromachining (LA-LBMM) process is advanced machining process which can overcome the limitations of traditional laser beam machining processes. LA-LBMM process uses a layer of a liquid medium such as water above the substrate surface during the application of laser beam
promoting their femtosecond laser machining processes. Figure 1: Chirped pulse amplification (CPA); how to build an ultra-short laser pulse. As with most new technologies, the first femtosecond lasers were expensive and often unreliable.
Laser cutting is a thermal separation process. Our pulsed Nd: YAG and fiber lasers permit a controlled heat entry which is optimum for fine cutting. The high peak performance of our laser permits a maximum cut depth of up to 10mm. As the laser beam can be focused on a very small diameter for high precision, fine cuts are possible with a minimum cut width of up to 15 µm (0.0006 in). In
Laser Beam Machining (LBM) is thermal processes considering the mechanisms of material removal. This in turn results in melting and vaporisation of the work material and finally material removal. Laser Beam Machining or more broadly laser material processing deals with machining and material processing like heat treatment. .
Electron-Beam Machining Process Figure 27.15 Schematic illustration of the electron-beam machining process. Unlike LBM, this process requires a vacuum, so workpiece size is limited to the size of the vacuum chamber.
Laser-beam machining is a thermal material-removal process that utilizes a high-energy, coherent light beam to melt and vaporize particles on the surface of metallic and non-metallic work pieces. Lasers can be used to cut, drill, weld and mark. LBM is particularly suitable for making accurately placed holes.
Laser Beam Machining Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical
CASE STUDY FIBER LASER CUTTING OF 3D STAMPINGS DEEP
Laser Micro-machining The laser beam is characterized by the half divergence angle θ micromachining process is one on a different time scale. Miliseconds 1×10-3 second Microseconds 1×10-6 second Nanoseconds 1×10-9 second Picoseconds 1×10-12 second Femtoseconds 1×10-15 second In other words, a femtosecond is a million times shorter than a nanosecond. Femtosecond …
Nd:YAG laser beam machining (LBM) process has a great potential to manufacture intricate shaped microproducts with its unique characteristics. In practical applications, such as drilling, grooving, cutting, or scribing, the optimal combination of Nd:YAG LBM process parameters needs to …
An overview is given of the state of the art of laser beam machining in general with special emphasis on applications of short and ultrashort lasers. In laser welding the trend is to apply optical sensors for process …
Welding . Cladding . Alloying . Laser Beam welding. LBW is a versatile process, capable of welding carbon steels, HSLA steels, stainless steel, aluminum,
Multi-objective Optimization of Laser Beam Machining Process Parameters 259 The experimental set up used for data collection is as given below: Machine
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter IJIRST
Lecture 12 Micromachining with Laser
Processes require transfer of energy from the laser beam to the work piece. Cutting process essentially consists of removing material. Laser cutting is done with the assistance of air, oxygen or dry nitrogen gas jet. The role of the jet is to cool the surface of the material and blow away the debris from the cutting zone. An arrangement for a gas-laser cutter. Advantages Laser cutting is
industries such as beam machining process (laser beam machining, electron beam machining, plasma beam machining), electro discharge machining, ultrasonic machining, electro chemical machining, jet machining processes (water jet machining, abrasive jet
Electron-Beam Machining Process Figure 27.15 Schematic illustration of the electron-beam machining process. Unlike LBM, this process requires a vacuum, so workpiece size is limited to the size of the vacuum chamber.
significance of various laser beam machining processes on Inconel alloys and also a brief study has been done on the effects of various element composition on the Inconel properties. An overview of research works on Inconel alloys using laser beam
Laser cutting is a thermal separation process. Our pulsed Nd: YAG and fiber lasers permit a controlled heat entry which is optimum for fine cutting. The high peak performance of our laser permits a maximum cut depth of up to 10mm. As the laser beam can be focused on a very small diameter for high precision, fine cuts are possible with a minimum cut width of up to 15 µm (0.0006 in). In
LASER CUTTING: FROM FIRST PRINCIPLES TO THE STATE OF THE ART Dr J. Powell1 and Dr A. Kaplan2 laser beam as shown in fig 1. (N.B. With certain materials this gas jet can accelerate the cutting process by doing chemical as well as physical work. For example, Carbon or mild steels are generally cut in a jet of pure oxygen. The oxidation process initiated by the laser heating generates …
A method for laser beam machining, in particular laser beam welding of bodywork components (14), with the aid of a remote laser head (3). The laser head is guided by a …
This chapter introduces two nontraditional machining processes: laser machining and electron beam machining (EBM). These two machining processes use laser and electron beams as energy sources to introduce thermal energy to remove work material by melting and/or vaporization.
Experimental Investigation and Analysis of Process
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter IJIRST
promoting their femtosecond laser machining processes. Figure 1: Chirped pulse amplification (CPA); how to build an ultra-short laser pulse. As with most new technologies, the first femtosecond lasers were expensive and often unreliable.
Multi-objective Optimization of Laser Beam Machining Process Parameters 259 The experimental set up used for data collection is as given below: Machine
Nd:YAG laser beam machining (LBM) process has a great potential to manufacture intricate shaped microproducts with its unique characteristics. In practical applications, such as drilling, grooving, cutting, or scribing, the optimal combination of Nd:YAG LBM process parameters needs to …
Laser beam machining (LBM) is one of the most widely used thermal energy based non-contact type advance machining process which can be applied for almost whole range of materials.
The polarization, reflection, absorption and trasmission of laser beam has practical meaning in laser machining processes and were discussed in section 2.8, 2.9. Besides common industrial lasers introduced in level 1, excimer lasers, semiconductor lasers are reviewed.
ME 677: Laser Material Processing Instructor: Ramesh Singh Laser Soldering and Brazing •In the laser soldering and brazing processes, the beam is used to melt a filler addition,
Laser Beam Machining – The Lasing Process • Lasing process describes the basic operation of laser, i.e. generation of coherent beam of light by
Laser beam machining (LBM) is a widely used thermal advance machining process capable of high accuracy machining of almost any material with complex geometries.
Modern Machining UNIT 5 MODERN MACHINING METHOD Method 5.3 Non-conventional Machining Processes 5.4 Electrical Discharge Machining 5.5 Wire Cut Electric Discharge Machining 5.6 Ultrasonic Machining 5.7 Chemical Machining Processes 5.8 Electrochemical Machining 5.9 Laser Beam Machining 5.10 Plasma Arc Machining 5.11 Summary 5.12 Answers to SAQs 5.1 INTRODUCTION Modern machining …
The Advantages of AWJM Compared with other Machining Processes A. Advantages of AWJM compared with Lasers Beam Machining (LBM) Laser cutting involves using a laser focused on material to melt, burn, or vaporize the material. The laser can be a gas laser (such as CO2) or a solid-state laser. The laser beam can be static, and the material moves infront of the laser, or the laser …
Parametric Optimization of NdYAG Laser Beam Machining
CASE STUDY FIBER LASER CUTTING OF 3D STAMPINGS DEEP
Liquid Assisted Laser Beam Micromachining (LA-LBMM) process is advanced machining process which can overcome the limitations of traditional laser beam machining processes. LA-LBMM process uses a layer of a liquid medium such as water above the substrate surface during the application of laser beam
An overview is given of the state of the art of laser beam machining in general with special emphasis on applications of short and ultrashort lasers. In laser welding the trend is to apply optical sensors for process …
2/02/2013 · I’ve just added a PDF file to the Knowledge Base to accompany my LBM (Laser Beam Machining) guide. It’s a 1 page overview covering the basics of the process.
Laser Micro-machining The laser beam is characterized by the half divergence angle θ micromachining process is one on a different time scale. Miliseconds 1×10-3 second Microseconds 1×10-6 second Nanoseconds 1×10-9 second Picoseconds 1×10-12 second Femtoseconds 1×10-15 second In other words, a femtosecond is a million times shorter than a nanosecond. Femtosecond …
Laser beam machining (LBM) is one of the most widely used thermal energy based non-contact type advance machining process which can be applied for almost whole range of materials.
Introduction of Laser Machining Processes AML
Finite element analysis and simulation of liquid-assisted
3 Figure 2 Figure 2 depicts the process of metal spinning which Kryton performs on eight CNC machines. A disk of metal is rotated at high speed while a forming tool applies force to the disk.
significance of various laser beam machining processes on Inconel alloys and also a brief study has been done on the effects of various element composition on the Inconel properties. An overview of research works on Inconel alloys using laser beam
Electron-Beam Machining Process Figure 27.15 Schematic illustration of the electron-beam machining process. Unlike LBM, this process requires a vacuum, so workpiece size is limited to the size of the vacuum chamber.
beam machining (LBM) processes [ ]. e LBM, which is a thermal energy-based machining process, is now being widely applied to ful ll the present day requirements of high
The cost of cutting hard-to-machine materials by conventional mechanical machining processes is high due to the low material removal rate and short tool life, and some materials are not possible to be cut by the conventional machining process at all. Laser beam machining is the machining processes
This chapter introduces two nontraditional machining processes: laser machining and electron beam machining (EBM). These two machining processes use laser and electron beams as energy sources to introduce thermal energy to remove work material by melting and/or vaporization.
Nd:YAG laser beam machining (LBM) process has a great potential to manufacture intricate shaped microproducts with its unique characteristics. In practical applications, such as drilling, grooving, cutting, or scribing, the optimal combination of Nd:YAG LBM process parameters needs to …
Today we have learned about Laser Beam Machining-Principle, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Application of Laser Beam Machining. If I have missed something, kindly inform me through commenting. If you
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter Optimization www.ijirst.org
Laser-beam machining is a thermal material-removal process that utilizes a high-energy, coherent light beam to melt and vaporize particles on the surface of metallic and non-metallic work pieces. Lasers can be used to cut, drill, weld and mark. LBM is particularly suitable for making accurately placed holes.
Laser beam machining is a form of non-traditional machining that can machine almost any known materials. It is It is thermal, non-contact process, which does …
A high energy-density laser beam vaporises the workpiece during the welding process to form a hole (keyhole), which allows the laser beam to penetrate into the metal to produce a deep, narrow melt pool.
Laser and Electron Beam Machining SpringerLink
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter IJIRST
machining process at all. Laser beam machining is the machining processes involving a laser beam as a heat source. It is a thermal process used to remove materials without mechanical engagement with workpiece material where the workpiece is heated to melting or boiling point and removed by melt ejection, vaporization, or ablation mechanisms. In contrast with a conventional …
Nd:YAG laser beam machining (LBM) process has a great potential to manufacture intricate shaped microproducts with its unique characteristics. In practical applications, such as drilling, grooving, cutting, or scribing, the optimal combination of Nd:YAG LBM process parameters needs to …
This slide contains the working process of Laser, their types and how they are used for machining purposes. Contents Laser Beam Machining Laser Type of Laser Laser Application Parameters Affecting LBM Advantage Disadvantage References 2 3. What is Laser LASER is the acronym for Light Amplified Stimulated Emission of Radiation Laser is a device which generates or amplifies light …
Liquid Assisted Laser Beam Micromachining (LA-LBMM) process is advanced machining process which can overcome the limitations of traditional laser beam machining processes. LA-LBMM process uses a layer of a liquid medium such as water above the substrate surface during the application of laser beam
The adaptability of laser beam machining allows them to perform more than one function, and the wide range of industries that often use laser beam machining technology includes automakers and jewelers.
The cost of cutting hard-to-machine materials by conventional mechanical machining processes is high due to the low material removal rate and short tool life, and some materials are not possible to be cut by the conventional machining process at all. Laser beam machining is the machining processes
Laser and Electron Beam Machining SpringerLink
Introduction of Laser Machining Processes AML
Modern Machining UNIT 5 MODERN MACHINING METHOD Method 5.3 Non-conventional Machining Processes 5.4 Electrical Discharge Machining 5.5 Wire Cut Electric Discharge Machining 5.6 Ultrasonic Machining 5.7 Chemical Machining Processes 5.8 Electrochemical Machining 5.9 Laser Beam Machining 5.10 Plasma Arc Machining 5.11 Summary 5.12 Answers to SAQs 5.1 INTRODUCTION Modern machining …
and Laser Welding & Cutting Tim Morris Technical Sales Manager TRUMPF Inc., Laser Technology Center. Agenda 1. Basics of lasers 2. Basics of laser welding 3. Summary. Flexibility … > beam manipulation (beam switching and sharing) > variety of product geometries and materials > ease of back-up (especially YAG) Often faster than other techniques > high power density weld process > …
A high energy-density laser beam vaporises the workpiece during the welding process to form a hole (keyhole), which allows the laser beam to penetrate into the metal to produce a deep, narrow melt pool.
Processes require transfer of energy from the laser beam to the work piece. Cutting process essentially consists of removing material. Laser cutting is done with the assistance of air, oxygen or dry nitrogen gas jet. The role of the jet is to cool the surface of the material and blow away the debris from the cutting zone. An arrangement for a gas-laser cutter. Advantages Laser cutting is
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter Optimization www.ijirst.org
The adaptability of laser beam machining allows them to perform more than one function, and the wide range of industries that often use laser beam machining technology includes automakers and jewelers.
Laser beam machining (LBM) is one of the advanced machining processes which are used for shaping almost whole range of engineering materials. In LBM, surface roughness is one of important response which affects the quality characteristics of product. In this research work, the effect of process parameters such as cutting speed, frequency and duty cycle on surface roughness (Ra) for …
beam machining (LBM) processes [ ]. e LBM, which is a thermal energy-based machining process, is now being widely applied to ful ll the present day requirements of high
In laser beam machining, the main concern is the machining quality as kerf width of the end product. It is essential for industrial It is essential for industrial applications to …
beam machining process uses highly coherent light source. beam can be focused by means of a lens on a very small spot in the work piece. This high power radiation of laser gives rise to high temperature on a small area of work piece.
Welding . Cladding . Alloying . Laser Beam welding. LBW is a versatile process, capable of welding carbon steels, HSLA steels, stainless steel, aluminum,
Laser Beam Machining A Literature Review on Heat affected
Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Liquid-Assisted
3 Figure 2 Figure 2 depicts the process of metal spinning which Kryton performs on eight CNC machines. A disk of metal is rotated at high speed while a forming tool applies force to the disk.
An overview is given of the state of the art of laser beam machining in general with special emphasis on applications of short and ultrashort lasers. In laser welding the trend is to apply optical sensors for process …
Liquid Assisted Laser Beam Micromachining (LA-LBMM) process is advanced machining process which can overcome the limitations of traditional laser beam machining processes. LA-LBMM process uses a layer of a liquid medium such as water above the substrate surface during the application of laser beam
The polarization, reflection, absorption and trasmission of laser beam has practical meaning in laser machining processes and were discussed in section 2.8, 2.9. Besides common industrial lasers introduced in level 1, excimer lasers, semiconductor lasers are reviewed.
Nd:YAG laser beam machining (LBM) process has a great potential to manufacture intricate shaped microproducts with its unique characteristics. In practical applications, such as drilling, grooving, cutting, or scribing, the optimal combination of Nd:YAG LBM process parameters needs to …
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter Optimization www.ijirst.org
Laser Micro-machining The laser beam is characterized by the half divergence angle θ micromachining process is one on a different time scale. Miliseconds 1×10-3 second Microseconds 1×10-6 second Nanoseconds 1×10-9 second Picoseconds 1×10-12 second Femtoseconds 1×10-15 second In other words, a femtosecond is a million times shorter than a nanosecond. Femtosecond …
Laser Beam Machining. Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. . Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. . Author Information
beam machining process uses highly coherent light source. beam can be focused by means of a lens on a very small spot in the work piece. This high power radiation of laser gives rise to high temperature on a small area of work piece.
Laser Beam Machining. Laser beam machining (LBM) is a thermal energy based advanced machining process in which the material is removed by (i) melting, (ii) vaporization, and (iii) chemical degradation (chemical bonds are broken which causes the materials to degrade).
Laser beam machining (LBM) is one of the most widely used thermal energy based non-contact type advance machining process which can be applied for almost whole range of materials.
A method for laser beam machining, in particular laser beam welding of bodywork components (14), with the aid of a remote laser head (3). The laser head is guided by a …
Laser drilling is a process of removing solid material by irradiating it with a pulsed laser beam. The depth over which the amount of material ca ne removed in a single laser pulse depends mainly on the optical properties of the material and the laser wavelength. This process utilizes focused and pulsed UV-light to drill holes into the wafers. Consecutive sequences of laser pulses are focused
A Fuzzy Logic-Based Prediction Model for Kerf Width in
Laser beam machining—A review Request PDF
Laser-beam machining is a thermal material-removal process that utilizes a high-energy, coherent light beam to melt and vaporize particles on the surface of metallic and non-metallic work pieces. Lasers can be used to cut, drill, weld and mark. LBM is particularly suitable for making accurately placed holes.
Processes require transfer of energy from the laser beam to the work piece. Cutting process essentially consists of removing material. Laser cutting is done with the assistance of air, oxygen or dry nitrogen gas jet. The role of the jet is to cool the surface of the material and blow away the debris from the cutting zone. An arrangement for a gas-laser cutter. Advantages Laser cutting is
Multi-objective Optimization of Laser Beam Machining Process Parameters 259 The experimental set up used for data collection is as given below: Machine
This slide contains the working process of Laser, their types and how they are used for machining purposes. Contents Laser Beam Machining Laser Type of Laser Laser Application Parameters Affecting LBM Advantage Disadvantage References 2 3. What is Laser LASER is the acronym for Light Amplified Stimulated Emission of Radiation Laser is a device which generates or amplifies light …
Laser Beam Machining A Literature Review on Heat affected
PDPM IIITDM JABALPUR WordPress.com
A high energy-density laser beam vaporises the workpiece during the welding process to form a hole (keyhole), which allows the laser beam to penetrate into the metal to produce a deep, narrow melt pool.
beam machining (LBM) processes [ ]. e LBM, which is a thermal energy-based machining process, is now being widely applied to ful ll the present day requirements of high
Thermal cutting processes differ from mechanical cutting (machining) in that the cutting action is initiated either by chemical reaction (oxidation) or melting (heat from arc).
In laser beam machining, the main concern is the machining quality as kerf width of the end product. It is essential for industrial It is essential for industrial applications to …
Laser beam machining is a form of non-traditional machining that can machine almost any known materials. It is It is thermal, non-contact process, which does …
CASE STUDY FIBER LASER CUTTING OF 3D STAMPINGS DEEP
Laser Beam Machining Knowles – – Major Reference Works
Abstract— Laser beam forming, a non-contact manufacturing process has become a viable manufacturing process for shaping metallic components.
PDPM IIITDM JABALPUR LASER Beam Machining Advancements ME 306 ADVANCED MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Submitted To Dr. TVK Gupta Submitted By: …
Laser-beam machining is a thermal material-removal process that utilizes a high-energy, coherent light beam to melt and vaporize particles on the surface of metallic and non-metallic work pieces. Lasers can be used to cut, drill, weld and mark. LBM is particularly suitable for making accurately placed holes.
Laser Micro-machining The laser beam is characterized by the half divergence angle θ micromachining process is one on a different time scale. Miliseconds 1×10-3 second Microseconds 1×10-6 second Nanoseconds 1×10-9 second Picoseconds 1×10-12 second Femtoseconds 1×10-15 second In other words, a femtosecond is a million times shorter than a nanosecond. Femtosecond …
Modern Machining UNIT 5 MODERN MACHINING METHOD Method 5.3 Non-conventional Machining Processes 5.4 Electrical Discharge Machining 5.5 Wire Cut Electric Discharge Machining 5.6 Ultrasonic Machining 5.7 Chemical Machining Processes 5.8 Electrochemical Machining 5.9 Laser Beam Machining 5.10 Plasma Arc Machining 5.11 Summary 5.12 Answers to SAQs 5.1 INTRODUCTION Modern machining …
Nd:YAG laser beam machining (LBM) process has a great potential to manufacture intricate shaped microproducts with its unique characteristics. In practical applications, such as drilling, grooving, cutting, or scribing, the optimal combination of Nd:YAG LBM process parameters needs to …
ME 677: Laser Material Processing Instructor: Ramesh Singh Laser Soldering and Brazing •In the laser soldering and brazing processes, the beam is used to melt a filler addition,
Laser Beam Machining or more broadly laser material processing deals with machining and material processing like heat treatment. the energy of the photon is absorbed by the work material leading to rapid substantial rise in local temperature. alloying. sheet metal bending. This in turn results in melting and vaporisation of the work material and finally material removal.
Review on Laser Beam Machining Process Parameter Optimization www.ijirst.org
machining process at all. Laser beam machining is the machining processes involving a laser beam as a heat source. It is a thermal process used to remove materials without mechanical engagement with workpiece material where the workpiece is heated to melting or boiling point and removed by melt ejection, vaporization, or ablation mechanisms. In contrast with a conventional …
LASER BEAM MACHINING PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Parametric Optimization of NdYAG Laser Beam Machining
Laser Beam Machining. Laser beam machining (LBM) is a thermal energy based advanced machining process in which the material is removed by (i) melting, (ii) vaporization, and (iii) chemical degradation (chemical bonds are broken which causes the materials to degrade).
Laser Beam Machining (LBM) is thermal processes considering the mechanisms of material removal. This in turn results in melting and vaporisation of the work material and finally material removal. Laser Beam Machining or more broadly laser material processing deals with machining and material processing like heat treatment. .
Electron-Beam Machining Process Figure 27.15 Schematic illustration of the electron-beam machining process. Unlike LBM, this process requires a vacuum, so workpiece size is limited to the size of the vacuum chamber.
3 Figure 2 Figure 2 depicts the process of metal spinning which Kryton performs on eight CNC machines. A disk of metal is rotated at high speed while a forming tool applies force to the disk.
promoting their femtosecond laser machining processes. Figure 1: Chirped pulse amplification (CPA); how to build an ultra-short laser pulse. As with most new technologies, the first femtosecond lasers were expensive and often unreliable.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Finite element analysis and simulation of liquid-assisted laser beam machining process Vinit Mistry 1 & Sagil James1 Received: 18 April 2017/Accepted: 17 August 2017/Published online: 7 September 2017
This slide contains the working process of Laser, their types and how they are used for machining purposes. Contents Laser Beam Machining Laser Type of Laser Laser Application Parameters Affecting LBM Advantage Disadvantage References 2 3. What is Laser LASER is the acronym for Light Amplified Stimulated Emission of Radiation Laser is a device which generates or amplifies light …
This chapter introduces two nontraditional machining processes: laser machining and electron beam machining (EBM). These two machining processes use laser and electron beams as energy sources to introduce thermal energy to remove work material by melting and/or vaporization.
PDPM IIITDM JABALPUR LASER Beam Machining Advancements ME 306 ADVANCED MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Submitted To Dr. TVK Gupta Submitted By: …
Laser-beam machining is a thermal material-removal process that utilizes a high-energy, coherent light beam to melt and vaporize particles on the surface of metallic and non-metallic work pieces. Lasers can be used to cut, drill, weld and mark. LBM is particularly suitable for making accurately placed holes.
2/02/2013 · I’ve just added a PDF file to the Knowledge Base to accompany my LBM (Laser Beam Machining) guide. It’s a 1 page overview covering the basics of the process.
Laser beam machining is a form of non-traditional machining that can machine almost any known materials. It is It is thermal, non-contact process, which does …
Experimental Investigation of Laser beam forming of
Laser Beam Machining Knowles – – Major Reference Works
Electron Beam Machining (EBM) is a thermal process. Here a steam of high speed electrons impinges on the work surface so that the kinetic energy of electrons is …
Lesson 40 Electron Beam and Laser Beam Machining Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur
Laser beam machining is a form of non-traditional machining that can machine almost any known materials. It is It is thermal, non-contact process, which does …
PDPM IIITDM JABALPUR LASER Beam Machining Advancements ME 306 ADVANCED MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Submitted To Dr. TVK Gupta Submitted By: …
Laser beam machining (LBM) is a widely used thermal advance machining process capable of high accuracy machining of almost any material with complex geometries.
Processes require transfer of energy from the laser beam to the work piece. Cutting process essentially consists of removing material. Laser cutting is done with the assistance of air, oxygen or dry nitrogen gas jet. The role of the jet is to cool the surface of the material and blow away the debris from the cutting zone. An arrangement for a gas-laser cutter. Advantages Laser cutting is
and Laser Welding & Cutting Tim Morris Technical Sales Manager TRUMPF Inc., Laser Technology Center. Agenda 1. Basics of lasers 2. Basics of laser welding 3. Summary. Flexibility … > beam manipulation (beam switching and sharing) > variety of product geometries and materials > ease of back-up (especially YAG) Often faster than other techniques > high power density weld process > …
Today we have learned about Laser Beam Machining-Principle, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Application of Laser Beam Machining. If I have missed something, kindly inform me through commenting. If you
Laser Beam Machining (LBM) is thermal processes considering the mechanisms of material removal. This in turn results in melting and vaporisation of the work material and finally material removal. Laser Beam Machining or more broadly laser material processing deals with machining and material processing like heat treatment. .
Applications of laser beam machining cutcnccam.com