Environmental implications of hydroxyl radicals oh pdf
ABSTRACTNoble metal nanoparticles (NPs) have been widely used in many consumer products. Their effects on the antioxidant activity of commercial dietary supplements have not been well evaluated. In this study, we examined the effects of gold (Au NPs), silver (Ag NPs), platinum (Pt NPs), and palladium (Pd NPs) on the hydroxyl radical (·OH
11.1 THE HYDROXYL RADICAL . 11 be titrated; CO, CH4, HCFCs, and other gases would accumulate to very high levels in the troposphere, with catastrophic environmental implications. A key factor preventing this catastrophe is the presence in the troposphere of trace levels of NOx (NOx NO + NO2) originating from combustion, lightning, and soils. The sources and sinks of NOx will be …
Cite this article: Djouider F. Radiation Induced OH• Free Radicals Degradation Process of Phenol in Aqueous Solutions – Environmental Implications.
Formation of hydroxyl radical (OH •) under microwave/H 2 O 2 is an important factor for removal of organic materials for deciding the role of OH • radicals. Tert-butyl ether (TBA) was used as a radical scavenger in oxidations processes.
Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of microparticles prepared from solid fermentation by edible-medicinal fungi. Z. Yuan, P. Yan* School of Municipal and Environment Egineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001, China . Received . February. 18, 2016; Revised July 26, 2016 Kelp waste is the main solid waste in kelp processing industries. Athe t the same time the hydroxyl •OH
Stefanic I, Ljubic I, Bonifacic M, Sabljic A, Asmus KD, Armstrong DA (2009) A surprisingly complex aqueous chemistry of the simplest amino acid—A pulse radiolysis and theoretical study on H/D kinetic isotope effects in the reaction of glycine anions with hydroxyl radicals.
The hydroxyl radical (• OH) is one of the most powerful oxidizing agents, able to react unselectively and instantaneously with the surrounding chemicals, including organic pollutants and inhibitors.
The hydroxyl (OH) radical initiated oxidation of these simple aromatics also produces a wide range of products including phenols, aromatic aldehydes and unsaturated carbonyl compounds. The secondary atmospheric chemistry of these oxygenated speices is largely unknown.
In the presence of FaSSGF and hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2), a particle size- and concentration-dependent generation of hydroxyl radicals (OH) was detected …
Reactions of hydroxyl radicals (• OH) with a number of RSNOs (S-nitroso derivatives of N-acetyl-dl-penicillamine, l-cysteinemethylester, N-acetylcysteamine, and dl-penicillamine) in aqueous medium at neutral and acidic pH have been reported in the present study. Radiation chemical technique (steady state and pulse radiolysis) has been utilized for the determination of the reaction rate
The (•)OH radicals are omnipresent in the environment (natural waters, atmosphere, interstellar space, etc. ), including biological systems where (•)OH has an important role in immunity metabolism. We provide an extensive view on the role of hydroxyl radical in different environmental compartments and in laboratory systems, with the aim of drawing more attention to this emerging issue
Formation of hydroxyl radical (·OH) in illuminated surface

Photolysis of graphene oxide in the presence of nitrate
Reported in this study are the results from a gas kinetics — aerosol laboratory study involving the OH induced oxidation of SO 2. At tropospheric and lower stratospheric pressures, reaction (1) is neither a third order process nor is it a simple bimolecular reaction.
26/03/2008 · Hydroxyl radical (OH •), the most reactive free radical in vivo, is formed by the reaction of O 2 •– with H 2 O 2 in the presence of Fe 2+ or Cu + (catalyst). This reaction is …
The rate of the attack by # OH radicals is typically 106 to 109 times faster than the corresponding reaction rate for molecular ozone. The major operating cost for
Read “Rate constants for the reactions of OH radicals with CF3CX=CY2 (X = H, F, CF3, Y = H, F, Cl), Environmental Science and Pollution Research” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
The toxicological implications of this heterogeneity in •OH formation by PM, as can be easily determined by ESR, need further investigation. Full Text The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF …
Nitrous oxide gas saturated samples were exposed to gamma radiation to isolate the effects of ˙OH, and para-chlorobenzoic acid was used to assess ˙OH exposure. This study found that the presence of molecular ozone versus the hydroxyl radical promoted N -nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) formation.
Aims: To determine the induction of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) by fine (<2.5 μm) and coarse (10–2.5 μm) particulate matter (PM) sampled over time at one sampling location, and to relate the observed effects to the hydroxyl radical (•OH) generating activities and transition metal content of these samples, and to meteorological parameters. Methods: Weekly samples of coarse and
The hydroxyl radical (OH) in indoor air: Sources and implications The hydroxyl radical (OH) in indoor air: Sources and implications Gligorovski, Sasho; Wortham, Henri 2014-12-01 00:00:00 Considering that people spend on average 80–90% of their life indoors, indoor …
Free radicals (FRs) in biochar could induce OH generation, and ≈12 spins of FRs were consumed to produce one trapped [OH] molecule. The proposed mechanism of OH generation was that FRs in biochar transferred electrons to O 2 to produce the superoxide radical anion and hydrogen peroxide, which reacted further with FRs to produce OH.
The experimental conditions were such that formation of OH radicals from HO 2 radicals was of minor importance, and the OH radical formation yields given above refer to direct formation of OH radicals and not HO 2 radicals.

From this monitoring – and from modelling – scientists have inferred global daytime OH concentrations between 100 thousand and 20 million hydroxyl radicals per cm 3. At sea level pressure, this is equivalent to between 0.01 and 1 ppt (parts per trillion).
We have measured the concentration of hydroxyl radicals (OH) produced in the gas phase by a commercially available purifier for air and surfaces, using the time rate of decay of n-heptane added to an environmental chamber. The hydroxyl generator, an Odorox® BOSS™ model, produces the OH …
A New Mechanism for Hydroxyl Radical Production in Irradiated Nanoparticle Solutions Cécile Sicard-Roselli , Emilie Brun , Manon Gilles , Gérard Baldacchino , Colin Kelsey , Harold McQuaid , Chris Polin , Nathan Wdloar w , and ederick r F Currell* 1. Introduction Understanding the interaction between ionizing radia-tion and nanoparticles containing heavy atoms is important because such
Addition and Correction to Environmental Implications of Hydroxyl Radicals (•OH) Journal content Jan 08, 2018 Recommendations: n/a Published in
The •OH radicals are omnipresent in the environment (natural waters, atmosphere, interstellar space, etc.), including biological systems where •OH has an important role in immunity metabolism. We provide an extensive view on the role of hydroxyl radical in different environmental compartments and in laboratory systems, with the aim of drawing more attention to this emerging issue. Further
The hydroxyl radical adsorbs readily on both surfaces. The subsurface Si-O bonds are weakened during the adsorption resulting in surface layer destabilization. This destabilization leads directly to surface disintegration in the case of *OH/(0111) adsorption. The product of the surface disintegration and reconstruction is a surface terminated by silanol groups (Si-OH) and siloxyl radicals (Si
The gas phase reactions of hydroxyl radicals with a series of carboxylic acids over the temperature range 240–440 K Philippe Dagaut Chemical Kinetics Division, Center for Chemical Physics, National Bureau of Standards, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20899
1/01/2012 · Generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) – including superoxide (• O 2 −), hydrogen peroxide (HOOH), and hydroxyl radical (• OH) – has been suggested as one mechanism underlying the adverse health effects caused by ambient particulate matter (PM).
Part 1: Oxidation and OH radicals Oxidation in the Atmosphere Many chemical compounds are emitted into the atmosphere but removal processes prevent them accumulating in the air.
Environmental Implications of Hydroxyl Radicals (center
airborne hydroxyl radicals are blocked by the skin, concerns have been raised in the past regarding the inhalation of airborne hydroxyl radicals and whether that could trigger the formation of biological free radicals.
Atmospheric chemistry at night Atmospheric chemistry is driven, in large part, by sunlight. Air pollution, for react with water vapour to produce hydroxyl radicals: O(1D) + H 2 O 2 OH [R2] Reaction with oxidants such as OH is typically the rate
Formation of insoluble aggregates under the influence of hydroxyl radicals is due to a limited reduction of intramolecular disulfide bridges followed by exposure of buried hydrophobic epitopes leading to the formation of extremely strong intermolecular bonds.
INTRODUCTION. Earth’s atmosphere is an oxidizing medium that drives organic molecules toward carbon dioxide, and oxidation by hydroxyl radicals (OH) initiates most of these reactions (1, 2).
The ( )OH radicals are omnipresent in the environment (natural waters, atmosphere, interstellar space, etc.), including biological systems where ( )OH has an important role in immunity metabolism. In this study, the authors provide an extensive view on the role of hydroxyl radical in different environmental compartments and in laboratory systems, with the aim of drawing more attention to this
International audienceThe hydroxyl radical (center dot OH) is one of the most powerful oxidizing agents, able to react unselectively and instantaneously with the surrounding chemicals, including organic pollutants and inhibitors. The center dot OH radicals are omnipresent in the environment (natural
The hydroxyl radical, • OH, is the neutral form of the hydroxide ion (OH −). Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive (easily becoming hydroxyl groups) and consequently short-lived; however, they form an important part of radical chemistry . [2]
Environmental-like chemicals, such as para-nonylphenol or bisphenol A, significantly stimulated hydroxyl radical (•OH) formation in the striatum. Allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, prevents para-nonylphenol and MPP + -induced •OH generation.
Gas-phase photolytic production of hydroxyl radicals in an
The hydroxyl nightglow has been examined anew using calculated rate constants for the key reactive and inelastic O + OH(<i>v</i>’) quenching processes. These constants have been obtained from quasiclassical trajectories run on the adiabatic ab initio-based double many-body expansion-IV
Hydroxyl (OH) and peroxy radicals (HO 2, RO 2) were measured in the Pearl River Delta which is one of the most polluted areas in China, in autumn 2014. The radical observations were complemented by measurements of OH reactivity (inverse OH lifetime) and a comprehensive set of trace gases including CO, NO x and VOCs.
Request PDF on ResearchGate On Dec 1, 2014, Sasho Gligorovski and others published The hydroxyl radical (OH) in indoor air: Sources and implications . We use cookies to make interactions with
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is considered to act as an antioxidant. However, the inhibitory effects of CGA on specific radical species are not well understood. Electron spin resonance (ESR) in combination with spin trapping techniques was utilized to detect free radicals. 5,5-Dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide
CONCLUSIONS: PM10 particles generate the hydroxyl radical, a highly deleterious free radical, in aqueous solution. This occurs by an iron dependent process and hydroxyl radicals could play a part in the pathogenicity of PM10 particles. Iron release was greatest at the pH of the lysosome (pH 4.6) indicating that iron may be mobilised inside macrophages after phagocytosis, leading to oxidative
Salinity is a widespread environmental stress that severely limits crop yield worldwide. Cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria) have the unique capability of catalytically reducing levels of stress-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) including hydroxyl radicals (˙OH…
hydroxyl radicals, i.e., OH, by the optical emission spectroscopy, as well as its density generated from the atmospheric bioplasma jet by the ultraviolet (UV) absorption spectroscopy, respectively. Figure3shows the schematic experimental setup for the ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy.
Addition and Correction to Environmental Implications of

The hydroxyl radical (OH) in indoor air Sources and
Abstract. Hydroxyl radicals (OH) are a key species in atmospheric photochemistry. In the lower atmosphere, up to ~30% of the primary OH radical production is attributed to the photolysis of nitrous acid (HONO), and field observations suggest a large missing source of HONO.
Theoretical calculations show that the dissociation of the Si–O–Si bonds is more favorable when catalyzed by hydroxyl free radicals (•OH) (7, 8); •OH species are highly active in organic synthesis , polymerization , and modification of proteins .
The ·OH formation rates were calculated from the measured phenol formation rates. Steady‐state concentrations of ·OH were measured by the addition of 5 × 10 …
Hydroxyl radical Wikipedia
Lipid Oxidation and its Implications to Food Quality and
D. Pezo, J. Salafranca and C. Nerín, Design of a method for generation of gas-phase hydroxyl radicals, and use of HPLC with fluorescence detection to assess the antioxidant capacity of natural essential oils, Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 385, 7, (1241), (2006).
of hydroxyl radicals, a reaction of water and organic radicals, previously formed in the interaction of an excited uranyl ion and a spin trap, was proposed. 16 The aim of this work was to investigate the production of hydroxyl radicals
Lipid Oxidation and its Implications to Food Quality and Human Health Dong Uk Ahn Animal Science Department. Iowa State University. Introduction • Process of Lipid Oxidation • Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species • Implications of Lipid Oxidation • Foods • Human Health • Biological Antioxidant Defense Systems • Antioxidants in Food Processing. Lipid Oxidation • Oxidative
hydroxyl radicals by an antioxidant, ascorbic acid, attenuates both the MDMA-induced depletion of 5-HT and the functional consequences associated with this depletion. Treatment of rats with ascorbic acid suppressed the generation of hydroxyl radicals, as
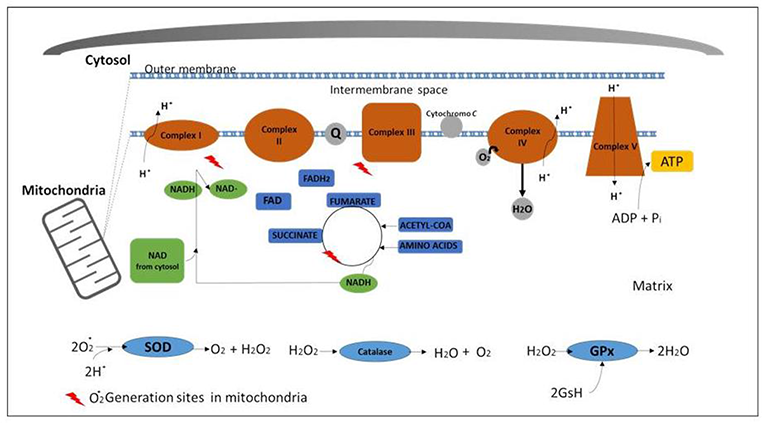
Abstract: As a result of the adaptation of life to an aerobic environment, nature has evolved a panoply of metalloproteins for oxidative metabolism and protection against reactive oxygen species.
Hydroxyl radicals are secondary oxidants that can be produced from decomposed ozone. They are stronger oxidizing agents than ozone itself, as a matter of fact, they are
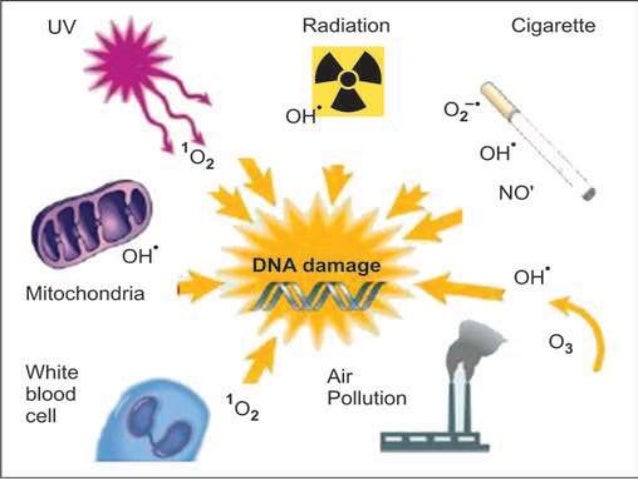
Hydroxyl radicals react with nucleic acids by hydrogen abstraction at the sugar or addition to the bases, both resulting in new radical moieties and de-polymerization [39, 40]. Inhaled particle-induced formation of • OH has been associated with genotoxicity [ 41 , 42 ] and oxidative stress [ 42 , 43 ].
One approach for treating phenol-containing water involves the oxidation of these compounds with hydroxyl radicals (•OH). •OH-based treatment technologies, such as the use of UV light to photolyze hydrogen peroxide (i.e., the UV/H 2 O 2 process), are becoming increasingly common in drinking water treatment, potable water reuse, and remediation of contaminated groundwater at hazardous waste
Hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and H2O2 were the dominant negative factors for the reduction because of their oxidizing effects, but these factors could be eliminated by the removal of ·OH. This work
Observations and Modeling of the Green Ocean Amazon 2014
2 radicals to regenerate OH and thereby maintain OH concentrations have been suggested, especially for forested regions dominatedbyisopreneemissions,suchasOHproductionfromthere-
DBHA is known to form as a result of the reaction of the hydroxyl radical with SA. A reaction mechanism is suggested to explain the enhanced SA removal by the hybrid process. A reaction mechanism is suggested to explain the enhanced SA removal by the hybrid process.
The hydroxyl radical, OH, is the neutral form of the hydroxide ion. Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive and consequently short-lived; however, they form an important part of radical chemistry.
radical (OH) and sulfuric acid quantifications. As part of the GoAmazon 2014/15 field campaign. As part of the GoAmazon 2014/15 field campaign. Hydroxyl radical determines tropospheric oxidation capacity and had been expected to be very low in the
Hydroxyl radicals react with nucleic acids by hydrogen abstraction at the sugar or addition to the bases, both resulting in new radical moieties and de-polymerization [39,40]. Inhaled particle-induced formation of • OH has been associated with genotoxicity [ 41 , 42 ] and oxidative stress [ 42 , 43 ].
Conclusion. While the exact mechanism or mechanisms of the hydrogen peroxide-to-hydroxyl radical conversion cannot be resolved on the basis of the experiments reported in this study, it is clear that the pyrite surface promotes the reaction.
Health effects depend on ozone precursors, which is a group of pollutants, primarily generated during the combustion of fossil fuels. Reaction with daylight ultraviolet (UV) rays and these precursors create ground-level ozone pollution (Tropospheric Ozone).
The ability of oxyhaemoglobin and methaemoglobin to generate hydroxyl radicals (OH.) from H2O2 has been investigated using deoxyribose and phenylalanine as ‘detector molecules’ for OH.. An excess of H2O2 degrades methaemoglobin, releasing iron ions that react with H2O2 to form a species that
Read “Photoformation of hydroxyl radical and hydrogen peroxide in aerosol particles from Alert, Nunavut: implications for aerosol and snowpack chemistry in the Arctic, Atmospheric Environment” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
a College of Environmental Science pathway of GO transformation changed from direct photolysis to indirect photolysis enhanced by the production of hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) during UV irradiation of nitrate. At environmentally relevant concentrations e.g., 1 mM), nitrate induced significant fragmentation of the GO nanostructure. The significant effects of ˙OH on GO morphology and surface
activity and hydroxyl radicals (OH) activity.DPPH scavenging activity of stem extracts of C. majus var. asiaticum was evaluated at 4.0 mg/ml was 55.8% and that of leaves was 23.3% at same concentration.
source of OH in the troposphere, but there are a number of other reactions (see for example reaction 14) and photolysis routes capable of forming OH directly or indirectly.
It is unknown whether hydroxyl radicals are produced in a similar way in interactions with bacteria, although this could have important ecological implications. The objective of this study was to develop an alternative method for hydroxyl radical detection in fungal growth systems and to investigate the potential use of the method in different environments, including soil.
One of the natural defence mechanisms for the removal of pollutants is the involvement of hydroxyl radical (OH), a potent reactive oxygen species in the atmosphere. It is generated either through photo-dissociation reactions or through some photocatalytic reactions.

Hydroxyl Radical an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of microparticles
“Detergent of the atmosphere” NIWA
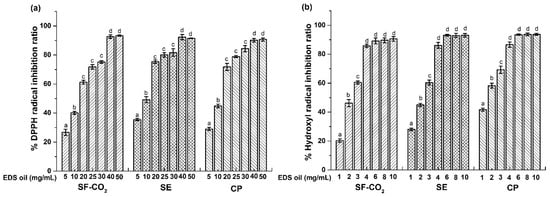
Effects of noble metal nanoparticles on the hydroxyl
Hydroxyl radical scavenging by cerium oxide nanoparticles
Environmental Estrogen-Like Chemicals and Hydroxyl
Lipid Oxidation and its Implications to Food Quality and
Addition and Correction to Environmental Implications of Hydroxyl Radicals (•OH) Journal content Jan 08, 2018 Recommendations: n/a Published in
ABSTRACTNoble metal nanoparticles (NPs) have been widely used in many consumer products. Their effects on the antioxidant activity of commercial dietary supplements have not been well evaluated. In this study, we examined the effects of gold (Au NPs), silver (Ag NPs), platinum (Pt NPs), and palladium (Pd NPs) on the hydroxyl radical (·OH
One of the natural defence mechanisms for the removal of pollutants is the involvement of hydroxyl radical (OH), a potent reactive oxygen species in the atmosphere. It is generated either through photo-dissociation reactions or through some photocatalytic reactions.
Formation of hydroxyl radical (OH •) under microwave/H 2 O 2 is an important factor for removal of organic materials for deciding the role of OH • radicals. Tert-butyl ether (TBA) was used as a radical scavenger in oxidations processes.
of hydroxyl radicals, a reaction of water and organic radicals, previously formed in the interaction of an excited uranyl ion and a spin trap, was proposed. 16 The aim of this work was to investigate the production of hydroxyl radicals
activity and hydroxyl radicals (OH) activity.DPPH scavenging activity of stem extracts of C. majus var. asiaticum was evaluated at 4.0 mg/ml was 55.8% and that of leaves was 23.3% at same concentration.
The •OH radicals are omnipresent in the environment (natural waters, atmosphere, interstellar space, etc.), including biological systems where •OH has an important role in immunity metabolism. We provide an extensive view on the role of hydroxyl radical in different environmental compartments and in laboratory systems, with the aim of drawing more attention to this emerging issue. Further
hydroxyl radicals, i.e., OH, by the optical emission spectroscopy, as well as its density generated from the atmospheric bioplasma jet by the ultraviolet (UV) absorption spectroscopy, respectively. Figure3shows the schematic experimental setup for the ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy.
Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of microparticles prepared from solid fermentation by edible-medicinal fungi. Z. Yuan, P. Yan* School of Municipal and Environment Egineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001, China . Received . February. 18, 2016; Revised July 26, 2016 Kelp waste is the main solid waste in kelp processing industries. Athe t the same time the hydroxyl •OH
DBHA is known to form as a result of the reaction of the hydroxyl radical with SA. A reaction mechanism is suggested to explain the enhanced SA removal by the hybrid process. A reaction mechanism is suggested to explain the enhanced SA removal by the hybrid process.
JHQHUDWHGIURPWKHDWPRVSKHULFSUHVVXUH ELRSODVPDMHW
Pyrite-induced hydroxyl radical formation and its effect
International audienceThe hydroxyl radical (center dot OH) is one of the most powerful oxidizing agents, able to react unselectively and instantaneously with the surrounding chemicals, including organic pollutants and inhibitors. The center dot OH radicals are omnipresent in the environment (natural
The hydroxyl radical, OH, is the neutral form of the hydroxide ion. Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive and consequently short-lived; however, they form an important part of radical chemistry.
Environmental-like chemicals, such as para-nonylphenol or bisphenol A, significantly stimulated hydroxyl radical (•OH) formation in the striatum. Allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, prevents para-nonylphenol and MPP -induced •OH generation.
Theoretical calculations show that the dissociation of the Si–O–Si bonds is more favorable when catalyzed by hydroxyl free radicals (•OH) (7, 8); •OH species are highly active in organic synthesis , polymerization , and modification of proteins .
One of the natural defence mechanisms for the removal of pollutants is the involvement of hydroxyl radical (OH), a potent reactive oxygen species in the atmosphere. It is generated either through photo-dissociation reactions or through some photocatalytic reactions.
One approach for treating phenol-containing water involves the oxidation of these compounds with hydroxyl radicals (•OH). •OH-based treatment technologies, such as the use of UV light to photolyze hydrogen peroxide (i.e., the UV/H 2 O 2 process), are becoming increasingly common in drinking water treatment, potable water reuse, and remediation of contaminated groundwater at hazardous waste
The hydroxyl radical adsorbs readily on both surfaces. The subsurface Si-O bonds are weakened during the adsorption resulting in surface layer destabilization. This destabilization leads directly to surface disintegration in the case of *OH/(0111) adsorption. The product of the surface disintegration and reconstruction is a surface terminated by silanol groups (Si-OH) and siloxyl radicals (Si
EPR study of the production of OH radicals in aqueous
Soil Nitrite as a Source of Atmospheric HONO and OH
Request PDF on ResearchGate On Dec 1, 2014, Sasho Gligorovski and others published The hydroxyl radical (OH) in indoor air: Sources and implications . We use cookies to make interactions with
Formation of insoluble aggregates under the influence of hydroxyl radicals is due to a limited reduction of intramolecular disulfide bridges followed by exposure of buried hydrophobic epitopes leading to the formation of extremely strong intermolecular bonds.
Reactions of hydroxyl radicals (• OH) with a number of RSNOs (S-nitroso derivatives of N-acetyl-dl-penicillamine, l-cysteinemethylester, N-acetylcysteamine, and dl-penicillamine) in aqueous medium at neutral and acidic pH have been reported in the present study. Radiation chemical technique (steady state and pulse radiolysis) has been utilized for the determination of the reaction rate
Hydroxyl radicals are secondary oxidants that can be produced from decomposed ozone. They are stronger oxidizing agents than ozone itself, as a matter of fact, they are
11.1 THE HYDROXYL RADICAL . 11 be titrated; CO, CH4, HCFCs, and other gases would accumulate to very high levels in the troposphere, with catastrophic environmental implications. A key factor preventing this catastrophe is the presence in the troposphere of trace levels of NOx (NOx NO NO2) originating from combustion, lightning, and soils. The sources and sinks of NOx will be …
Salinity is a widespread environmental stress that severely limits crop yield worldwide. Cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria) have the unique capability of catalytically reducing levels of stress-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) including hydroxyl radicals (˙OH…
The •OH radicals are omnipresent in the environment (natural waters, atmosphere, interstellar space, etc.), including biological systems where •OH has an important role in immunity metabolism. We provide an extensive view on the role of hydroxyl radical in different environmental compartments and in laboratory systems, with the aim of drawing more attention to this emerging issue. Further
hydroxyl radicals, i.e., OH, by the optical emission spectroscopy, as well as its density generated from the atmospheric bioplasma jet by the ultraviolet (UV) absorption spectroscopy, respectively. Figure3shows the schematic experimental setup for the ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy.
Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of microparticles prepared from solid fermentation by edible-medicinal fungi. Z. Yuan, P. Yan* School of Municipal and Environment Egineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001, China . Received . February. 18, 2016; Revised July 26, 2016 Kelp waste is the main solid waste in kelp processing industries. Athe t the same time the hydroxyl •OH
The ability of oxyhaemoglobin and methaemoglobin to generate hydroxyl radicals (OH.) from H2O2 has been investigated using deoxyribose and phenylalanine as ‘detector molecules’ for OH.. An excess of H2O2 degrades methaemoglobin, releasing iron ions that react with H2O2 to form a species that
The hydroxyl radical, • OH, is the neutral form of the hydroxide ion (OH −). Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive (easily becoming hydroxyl groups) and consequently short-lived; however, they form an important part of radical chemistry . [2]
The hydroxyl nightglow has been examined anew using calculated rate constants for the key reactive and inelastic O OH(<i>v</i>’) quenching processes. These constants have been obtained from quasiclassical trajectories run on the adiabatic ab initio-based double many-body expansion-IV
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is considered to act as an antioxidant. However, the inhibitory effects of CGA on specific radical species are not well understood. Electron spin resonance (ESR) in combination with spin trapping techniques was utilized to detect free radicals. 5,5-Dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide
In the presence of FaSSGF and hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2), a particle size- and concentration-dependent generation of hydroxyl radicals (OH) was detected …
Environmental Implications of Hydroxyl Radicals (center
EPR study of the production of OH radicals in aqueous
It is unknown whether hydroxyl radicals are produced in a similar way in interactions with bacteria, although this could have important ecological implications. The objective of this study was to develop an alternative method for hydroxyl radical detection in fungal growth systems and to investigate the potential use of the method in different environments, including soil.
Part 1: Oxidation and OH radicals Oxidation in the Atmosphere Many chemical compounds are emitted into the atmosphere but removal processes prevent them accumulating in the air.
Hydroxyl radicals are secondary oxidants that can be produced from decomposed ozone. They are stronger oxidizing agents than ozone itself, as a matter of fact, they are
The ·OH formation rates were calculated from the measured phenol formation rates. Steady‐state concentrations of ·OH were measured by the addition of 5 × 10 …
In the presence of FaSSGF and hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2), a particle size- and concentration-dependent generation of hydroxyl radicals (OH) was detected …
11.1 THE HYDROXYL RADICAL . 11 be titrated; CO, CH4, HCFCs, and other gases would accumulate to very high levels in the troposphere, with catastrophic environmental implications. A key factor preventing this catastrophe is the presence in the troposphere of trace levels of NOx (NOx NO NO2) originating from combustion, lightning, and soils. The sources and sinks of NOx will be …
Formation of hydroxyl radical (OH •) under microwave/H 2 O 2 is an important factor for removal of organic materials for deciding the role of OH • radicals. Tert-butyl ether (TBA) was used as a radical scavenger in oxidations processes.
Environmental-like chemicals, such as para-nonylphenol or bisphenol A, significantly stimulated hydroxyl radical (•OH) formation in the striatum. Allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, prevents para-nonylphenol and MPP -induced •OH generation.
a College of Environmental Science pathway of GO transformation changed from direct photolysis to indirect photolysis enhanced by the production of hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) during UV irradiation of nitrate. At environmentally relevant concentrations e.g., 1 mM), nitrate induced significant fragmentation of the GO nanostructure. The significant effects of ˙OH on GO morphology and surface
Request PDF on ResearchGate On Dec 1, 2014, Sasho Gligorovski and others published The hydroxyl radical (OH) in indoor air: Sources and implications . We use cookies to make interactions with
Hydroxyl (OH) and peroxy radicals (HO 2, RO 2) were measured in the Pearl River Delta which is one of the most polluted areas in China, in autumn 2014. The radical observations were complemented by measurements of OH reactivity (inverse OH lifetime) and a comprehensive set of trace gases including CO, NO x and VOCs.
1/01/2012 · Generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) – including superoxide (• O 2 −), hydrogen peroxide (HOOH), and hydroxyl radical (• OH) – has been suggested as one mechanism underlying the adverse health effects caused by ambient particulate matter (PM).
Abstract. Hydroxyl radicals (OH) are a key species in atmospheric photochemistry. In the lower atmosphere, up to ~30% of the primary OH radical production is attributed to the photolysis of nitrous acid (HONO), and field observations suggest a large missing source of HONO.
Hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and H2O2 were the dominant negative factors for the reduction because of their oxidizing effects, but these factors could be eliminated by the removal of ·OH. This work
Hydroxyl radical Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
Addition and Correction to Environmental Implications of
Hydroxyl radicals react with nucleic acids by hydrogen abstraction at the sugar or addition to the bases, both resulting in new radical moieties and de-polymerization [39,40]. Inhaled particle-induced formation of • OH has been associated with genotoxicity [ 41 , 42 ] and oxidative stress [ 42 , 43 ].
The hydroxyl radical, OH, is the neutral form of the hydroxide ion. Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive and consequently short-lived; however, they form an important part of radical chemistry.
of hydroxyl radicals, a reaction of water and organic radicals, previously formed in the interaction of an excited uranyl ion and a spin trap, was proposed. 16 The aim of this work was to investigate the production of hydroxyl radicals
Addition and Correction to Environmental Implications of Hydroxyl Radicals (•OH) Journal content Jan 08, 2018 Recommendations: n/a Published in
Hydroxyl radicals react with nucleic acids by hydrogen abstraction at the sugar or addition to the bases, both resulting in new radical moieties and de-polymerization [39, 40]. Inhaled particle-induced formation of • OH has been associated with genotoxicity [ 41 , 42 ] and oxidative stress [ 42 , 43 ].
From this monitoring – and from modelling – scientists have inferred global daytime OH concentrations between 100 thousand and 20 million hydroxyl radicals per cm 3. At sea level pressure, this is equivalent to between 0.01 and 1 ppt (parts per trillion).
Unexpected transformation of dissolved phenols to toxic
Formation of insoluble aggregates under the influence of hydroxyl radicals is due to a limited reduction of intramolecular disulfide bridges followed by exposure of buried hydrophobic epitopes leading to the formation of extremely strong intermolecular bonds.
Formation of OH radicals in the gas phase reactions of O3
Environmental Estrogen-Like Chemicals and Hydroxyl
Hydroxyl radical Wikipedia
The ability of oxyhaemoglobin and methaemoglobin to generate hydroxyl radicals (OH.) from H2O2 has been investigated using deoxyribose and phenylalanine as ‘detector molecules’ for OH.. An excess of H2O2 degrades methaemoglobin, releasing iron ions that react with H2O2 to form a species that
Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of microparticles